Top Cybersecurity Interview Questions for 2025 🔐 | CodeVisium
Prepare for your cybersecurity interview with the most important questions of 2025, including key concepts like symmetric vs. asymmetric encryption. Boost your InfoSec knowledge today!

CodeVisium
380 views • Sep 27, 2025
About this video
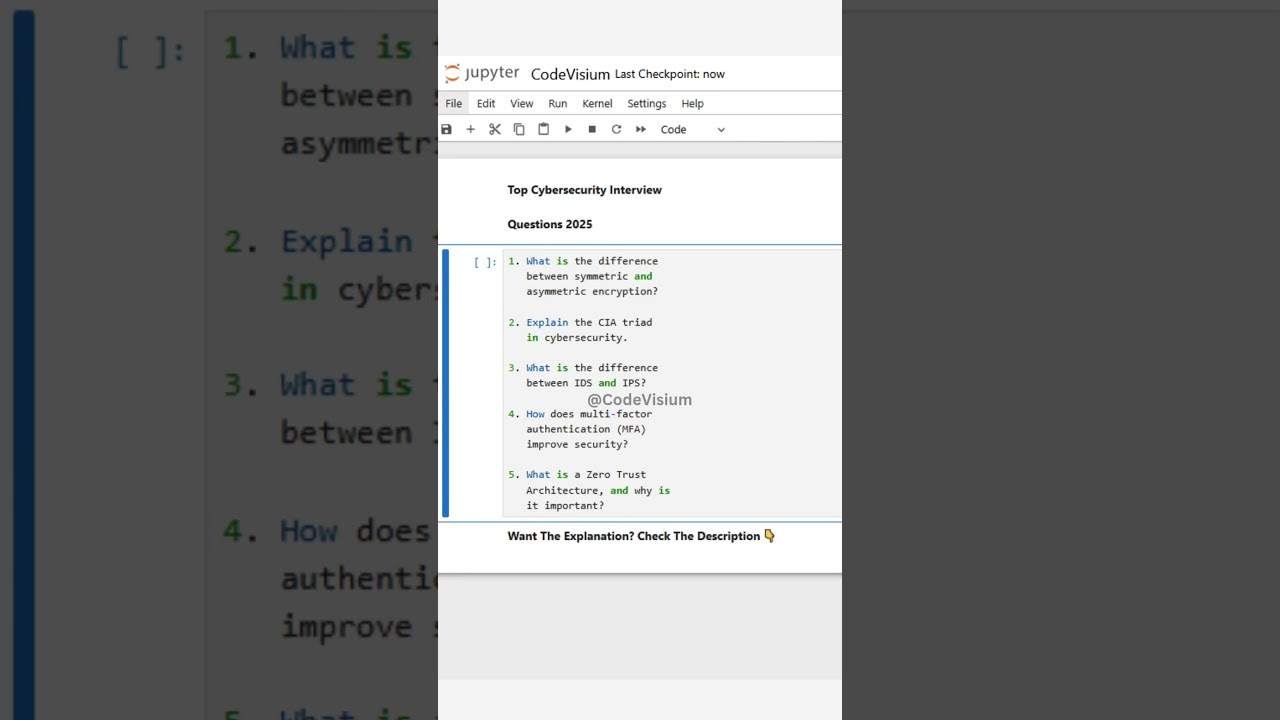
1. What is the difference between symmetric and asymmetric encryption?
Symmetric Encryption: Uses the same key for encryption and decryption (e.g., AES, DES). Fast but requires secure key sharing.
Asymmetric Encryption: Uses a public key for encryption and a private key for decryption (e.g., RSA, ECC). Slower but more secure for key exchange.
This question is crucial for roles like Security Engineer and Cryptographer, testing your grasp of encryption fundamentals.
2. Explain the CIA triad in cybersecurity.
Confidentiality: Ensuring only authorized users can access information (encryption, access control).
Integrity: Ensuring data is accurate and unaltered (hashing, digital signatures).
Availability: Ensuring systems and data are accessible when needed (backups, redundancy).
Every cybersecurity professional must understand the CIA triad since it’s the foundation of security policies.
3. What is the difference between IDS and IPS?
IDS (Intrusion Detection System): Monitors network traffic and alerts on suspicious activities. Passive in nature.
IPS (Intrusion Prevention System): Monitors and actively blocks malicious traffic. Proactive in nature.
Employers ask this to see if you can design systems that detect and prevent attacks.
4. How does multi-factor authentication (MFA) improve security?
MFA requires users to provide two or more factors:
Something you know (password).
Something you have (token, mobile).
Something you are (biometrics).
Even if one factor is compromised, the attacker cannot gain full access.
With the rise of phishing and credential theft, MFA is a critical layer of defense in 2025.
5. What is a Zero Trust Architecture, and why is it important?
Zero Trust = “Never trust, always verify.”
Instead of assuming devices or users inside a network are safe, Zero Trust continuously verifies them.
It uses least privilege access, segmentation, and continuous authentication.
This is becoming the gold standard in modern cybersecurity as remote work, IoT, and cloud computing expand attack surfaces.
Why These Questions Matter in 2025
Cybersecurity is one of the fastest-growing fields. With AI-powered cyberattacks, ransomware-as-a-service, cloud breaches, and state-sponsored hacking, companies want candidates who understand core principles and modern defense mechanisms.
Interviewers ask these questions to test:
Your encryption and cryptography fundamentals.
Knowledge of security frameworks (CIA triad, Zero Trust).
Ability to secure networks using IDS/IPS, MFA, and monitoring tools.
Roles like Cybersecurity Analyst, Ethical Hacker, Security Engineer, SOC Analyst, and Cloud Security Specialist rely heavily on these concepts.
By preparing these questions, you’ll stand out as someone who not only knows theory but can also apply security best practices in real-world systems.
#Cybersecurity #InfoSec #EthicalHacking #Hacking #SecurityEngineer #ZeroTrust #Encryption #MFA #CodeVisium
Symmetric Encryption: Uses the same key for encryption and decryption (e.g., AES, DES). Fast but requires secure key sharing.
Asymmetric Encryption: Uses a public key for encryption and a private key for decryption (e.g., RSA, ECC). Slower but more secure for key exchange.
This question is crucial for roles like Security Engineer and Cryptographer, testing your grasp of encryption fundamentals.
2. Explain the CIA triad in cybersecurity.
Confidentiality: Ensuring only authorized users can access information (encryption, access control).
Integrity: Ensuring data is accurate and unaltered (hashing, digital signatures).
Availability: Ensuring systems and data are accessible when needed (backups, redundancy).
Every cybersecurity professional must understand the CIA triad since it’s the foundation of security policies.
3. What is the difference between IDS and IPS?
IDS (Intrusion Detection System): Monitors network traffic and alerts on suspicious activities. Passive in nature.
IPS (Intrusion Prevention System): Monitors and actively blocks malicious traffic. Proactive in nature.
Employers ask this to see if you can design systems that detect and prevent attacks.
4. How does multi-factor authentication (MFA) improve security?
MFA requires users to provide two or more factors:
Something you know (password).
Something you have (token, mobile).
Something you are (biometrics).
Even if one factor is compromised, the attacker cannot gain full access.
With the rise of phishing and credential theft, MFA is a critical layer of defense in 2025.
5. What is a Zero Trust Architecture, and why is it important?
Zero Trust = “Never trust, always verify.”
Instead of assuming devices or users inside a network are safe, Zero Trust continuously verifies them.
It uses least privilege access, segmentation, and continuous authentication.
This is becoming the gold standard in modern cybersecurity as remote work, IoT, and cloud computing expand attack surfaces.
Why These Questions Matter in 2025
Cybersecurity is one of the fastest-growing fields. With AI-powered cyberattacks, ransomware-as-a-service, cloud breaches, and state-sponsored hacking, companies want candidates who understand core principles and modern defense mechanisms.
Interviewers ask these questions to test:
Your encryption and cryptography fundamentals.
Knowledge of security frameworks (CIA triad, Zero Trust).
Ability to secure networks using IDS/IPS, MFA, and monitoring tools.
Roles like Cybersecurity Analyst, Ethical Hacker, Security Engineer, SOC Analyst, and Cloud Security Specialist rely heavily on these concepts.
By preparing these questions, you’ll stand out as someone who not only knows theory but can also apply security best practices in real-world systems.
#Cybersecurity #InfoSec #EthicalHacking #Hacking #SecurityEngineer #ZeroTrust #Encryption #MFA #CodeVisium
Tags and Topics
Browse our collection to discover more content in these categories.
Video Information
Views
380
Likes
5
Duration
0:10
Published
Sep 27, 2025
Related Trending Topics
LIVE TRENDSRelated trending topics. Click any trend to explore more videos.