Master Decision Tree Strategy for Bidding: Should You Bid High or Low? 💡
Learn how to effectively solve a bidding problem using Decision Trees. This step-by-step guide covers bidding high or low, helping you make smarter decisions in competitive scenarios.

Joshua Emmanuel
16.6K views • Oct 4, 2022
About this video
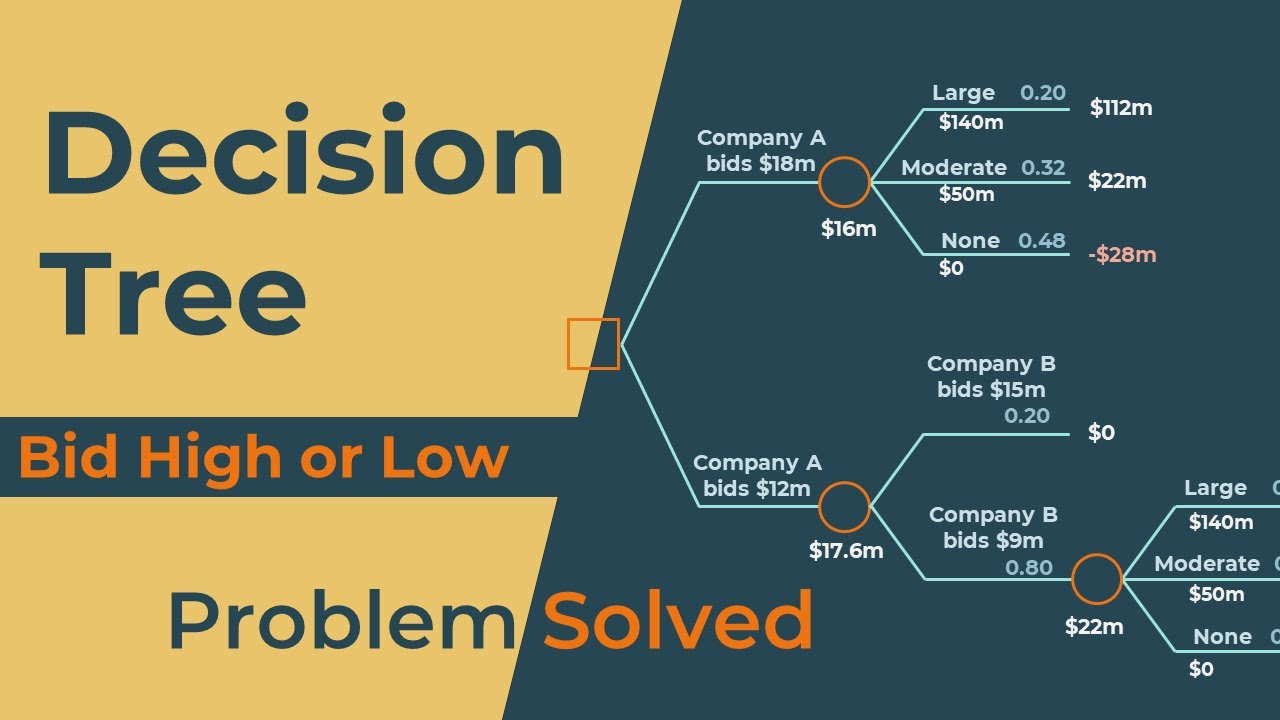
This video shows how to solve a Bid High or Low problem using Decision Tree.
00:00 Question to solve
00:56 Decision Tree - High Bid
02:22 Low Bid
03:25 Complete Tree
Problem:
Company A is deciding whether to place a high bid of $18 million
or a low bid of $12 million for leasing rights to a mining site.
A major competitor (Company B) is also bidding for the same leasing rights.
There is a 0.2 probability that Company B will place a $15 million bid
and a 0.8 probability that they will place a $9 million bid.
Preliminary examination of the site indicates a 0.20 probability of large deposits with net returns of $140 million,
a 0.32 probability of moderate deposits with $50 million net returns,
and a 0.48 probability of no deposits.
The company that wins the bid will incur additional $10 million in extraction costs.
a) How should Company A bid?
b) What is the expected value of the decision?
References: Spreadsheet Modeling and Decision Analysis: A Practical Introduction to Business Analytics, Cliff T. Ragsdale, Cengage Learning, 2017
Sensitivity Analysis in Decision Analysis: https://youtu.be/ybz5AAlyrLk
00:00 Question to solve
00:56 Decision Tree - High Bid
02:22 Low Bid
03:25 Complete Tree
Problem:
Company A is deciding whether to place a high bid of $18 million
or a low bid of $12 million for leasing rights to a mining site.
A major competitor (Company B) is also bidding for the same leasing rights.
There is a 0.2 probability that Company B will place a $15 million bid
and a 0.8 probability that they will place a $9 million bid.
Preliminary examination of the site indicates a 0.20 probability of large deposits with net returns of $140 million,
a 0.32 probability of moderate deposits with $50 million net returns,
and a 0.48 probability of no deposits.
The company that wins the bid will incur additional $10 million in extraction costs.
a) How should Company A bid?
b) What is the expected value of the decision?
References: Spreadsheet Modeling and Decision Analysis: A Practical Introduction to Business Analytics, Cliff T. Ragsdale, Cengage Learning, 2017
Sensitivity Analysis in Decision Analysis: https://youtu.be/ybz5AAlyrLk
Tags and Topics
Browse our collection to discover more content in these categories.
Video Information
Views
16.6K
Likes
213
Duration
4:18
Published
Oct 4, 2022
User Reviews
4.5
(3) Related Trending Topics
LIVE TRENDSRelated trending topics. Click any trend to explore more videos.
Trending Now