Unlocking Secure Communication: Quantum Key Distribution Protocols 🔐
Join Ludovic Noirie from Nokia Bell Labs France to explore the cutting-edge of quantum cryptography and how Quantum Key Distribution protocols revolutionize data security. Don't miss this insightful session!

Pupusse LINCS
191 views • Oct 24, 2022
About this video
Speaker: Ludovic Noirie (Nokia Bell Labs France).
Webpage: https://www.lincs.fr/events/quantum-cryptography-quantum-key-distribution-protocols/.
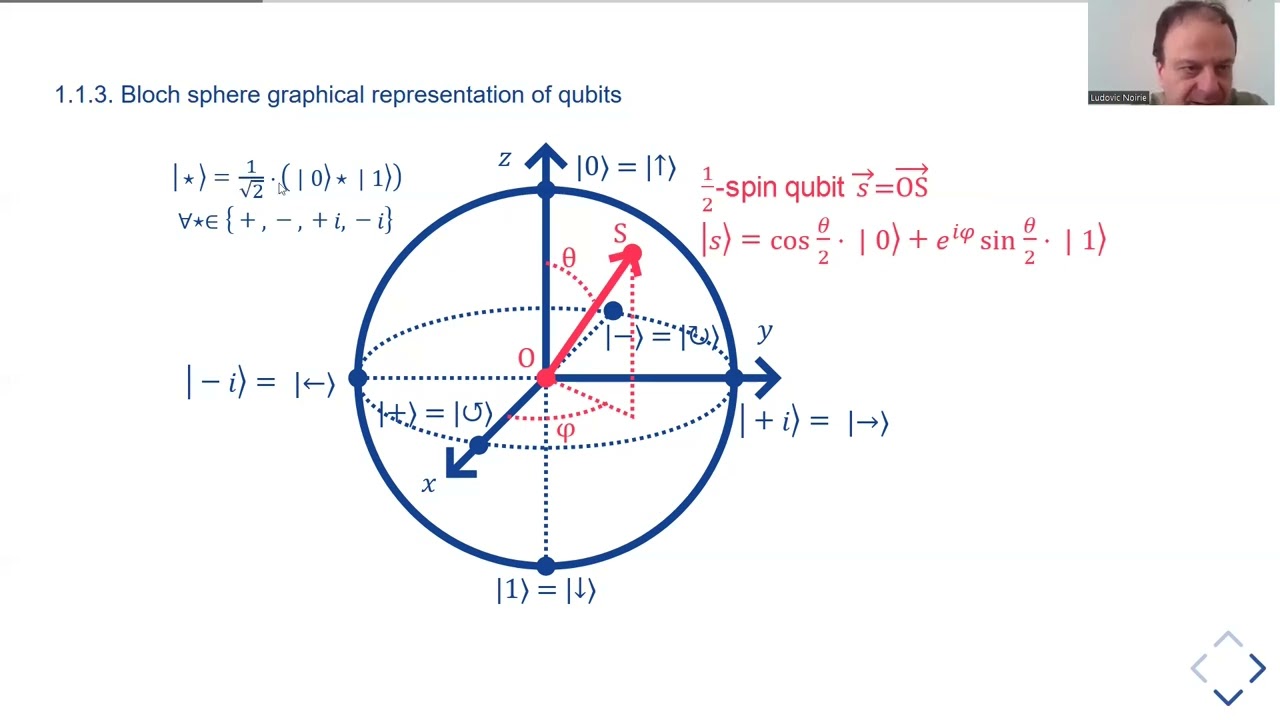
Quantum cryptography [BBE92] consists of the communication of a shared secret key between two users (Alice and Bob) which prevents an eavesdropper (Eve) from intercepting it without being detected, the security being proven by the principles of quantum physics. These mechanisms are called quantum key distribution (QKD) protocols.
In this talk, we will present the first QKD protocol proposed in 1984 by Bennet and Brassard [BB84], explaining how the protocol works and why Eve cannot intercept the distributed key without being detected. We will also briefly present another protocol proposed by Ekert in 1991 [Eke91]. This alternative protocol is based on the violation of Bell’s inequalities with quantum physics, a fact that led to the 2022 Nobel Prize in Physics for Alain Aspect, John Clauser and Anton Zeilinger [Nobel2022].
References:
[BB84] Charles H. Bennett and Gilles Brassard, “Quantum cryptography: Public key distribution and coin tossing”, in Proceedings of the International Conference on Computers, Systems and Signal Processing, pp. 175-179, Bangalore, 1984, republished in Theoretical Computer Science, vol. 560,? 2014, pp. 7–11, https://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.tcs.2014.05.025.
[Eke91] Artur K. Ekert, “Quantum cryptography based on Bell’s theorem”, Physical Review Letters, Vol. 67, no. 6, pp. 661-663, 1991, https://link.aps.org/doi/10.1103/PhysRevLett.67.661.
[BBE92] Charles H. Bennett, Gilles Brassard and Artur K. Ekert, “Quantum Cryptography”, Scientific American, vol. 267, no. 4, 1992, pp. 50–57, http://www.jstor.org/stable/24939253.
[Nobel2022] The Nobel Prize website, “The Nobel Prize in Physics 2022”, https://www.nobelprize.org/prizes/physics/2022/summary/.
See also Wikipedia:
– https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Quantum_cryptography,
– https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/BB84.
Webpage: https://www.lincs.fr/events/quantum-cryptography-quantum-key-distribution-protocols/.
Quantum cryptography [BBE92] consists of the communication of a shared secret key between two users (Alice and Bob) which prevents an eavesdropper (Eve) from intercepting it without being detected, the security being proven by the principles of quantum physics. These mechanisms are called quantum key distribution (QKD) protocols.
In this talk, we will present the first QKD protocol proposed in 1984 by Bennet and Brassard [BB84], explaining how the protocol works and why Eve cannot intercept the distributed key without being detected. We will also briefly present another protocol proposed by Ekert in 1991 [Eke91]. This alternative protocol is based on the violation of Bell’s inequalities with quantum physics, a fact that led to the 2022 Nobel Prize in Physics for Alain Aspect, John Clauser and Anton Zeilinger [Nobel2022].
References:
[BB84] Charles H. Bennett and Gilles Brassard, “Quantum cryptography: Public key distribution and coin tossing”, in Proceedings of the International Conference on Computers, Systems and Signal Processing, pp. 175-179, Bangalore, 1984, republished in Theoretical Computer Science, vol. 560,? 2014, pp. 7–11, https://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.tcs.2014.05.025.
[Eke91] Artur K. Ekert, “Quantum cryptography based on Bell’s theorem”, Physical Review Letters, Vol. 67, no. 6, pp. 661-663, 1991, https://link.aps.org/doi/10.1103/PhysRevLett.67.661.
[BBE92] Charles H. Bennett, Gilles Brassard and Artur K. Ekert, “Quantum Cryptography”, Scientific American, vol. 267, no. 4, 1992, pp. 50–57, http://www.jstor.org/stable/24939253.
[Nobel2022] The Nobel Prize website, “The Nobel Prize in Physics 2022”, https://www.nobelprize.org/prizes/physics/2022/summary/.
See also Wikipedia:
– https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Quantum_cryptography,
– https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/BB84.
Video Information
Views
191
Likes
5
Duration
01:12:58
Published
Oct 24, 2022
Related Trending Topics
LIVE TRENDSRelated trending topics. Click any trend to explore more videos.