Unlocking Quantum Complexity in Experimental Physics 🔬
Discover Jordan Cotler's groundbreaking framework at Harvard for analyzing the quantum complexity of experiments, paving the way for new insights in quantum physics research.

Centrum Fizyki Teoretycznej PAN
461 views • Apr 11, 2022
About this video
Jordan Cotler (Harvard University).
Quantum Complexity of Experiments.
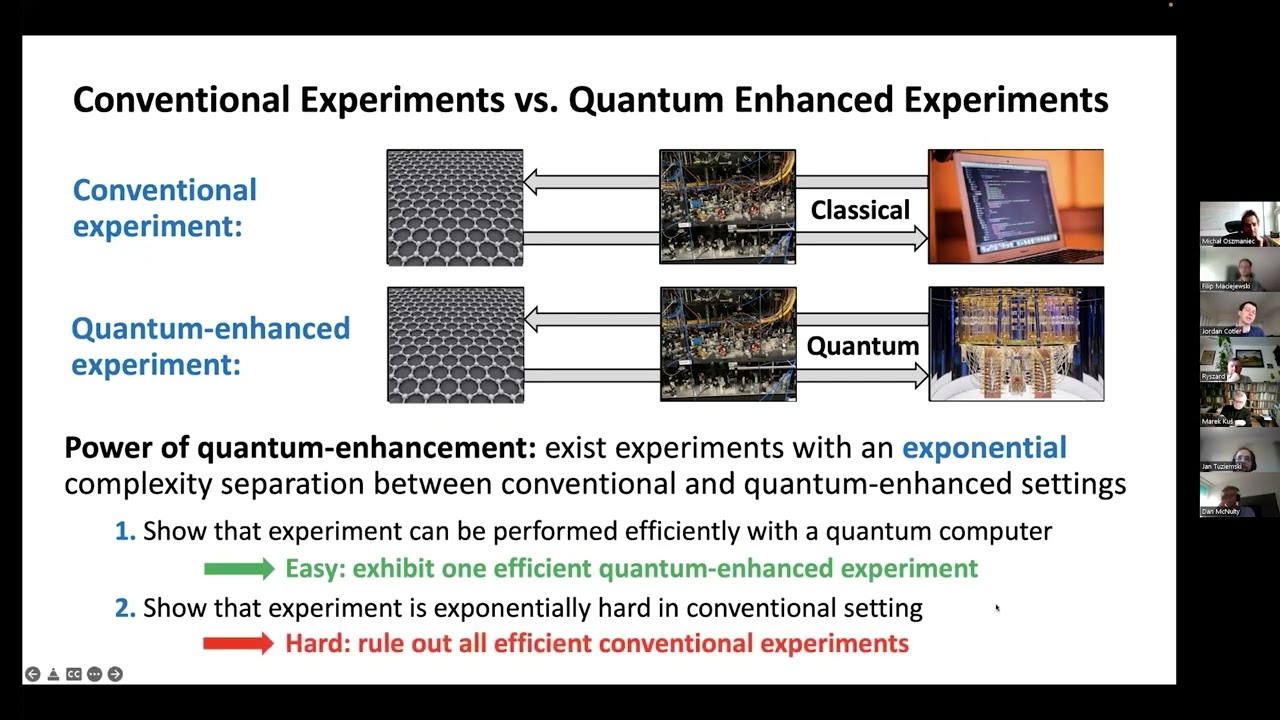
We introduce a theoretical framework to study experimental physics using quantum complexity theory. This allows us to address: what is the computational complexity of an experiment? For several 'model' experiments, we prove that there is an exponential savings in resources if the experimentalist can entangle apparatuses with experimental samples. A novel example is the experimental task of determining the symmetry class of a time evolution operator for a quantum many-body system. Some of our complexity advantages have been realized on Google's Sycamore processor, demonstrating a real-world advantage for learning algorithms with a quantum memory.
Team-Net QC Colloquium 2022.04.06
The purpose of the Team-Net Quantum Computing Colloquium series is to expose Polish and international researchers, as well as interested peers, to the most important recent achievements and trends in the field of quantum computing. Topics of the colloquium include, but are not limited to:
Near-term quantum algorithms
Quantum supremacy experiments
Resource-theoretic approaches to quantum computing
Quantum machine learning
Practical quantum error correction and error mitigation
Mathematical aspects of quantum computing and many body physics
webpage of the project: https://nisq.pl/
Quantum Complexity of Experiments.
We introduce a theoretical framework to study experimental physics using quantum complexity theory. This allows us to address: what is the computational complexity of an experiment? For several 'model' experiments, we prove that there is an exponential savings in resources if the experimentalist can entangle apparatuses with experimental samples. A novel example is the experimental task of determining the symmetry class of a time evolution operator for a quantum many-body system. Some of our complexity advantages have been realized on Google's Sycamore processor, demonstrating a real-world advantage for learning algorithms with a quantum memory.
Team-Net QC Colloquium 2022.04.06
The purpose of the Team-Net Quantum Computing Colloquium series is to expose Polish and international researchers, as well as interested peers, to the most important recent achievements and trends in the field of quantum computing. Topics of the colloquium include, but are not limited to:
Near-term quantum algorithms
Quantum supremacy experiments
Resource-theoretic approaches to quantum computing
Quantum machine learning
Practical quantum error correction and error mitigation
Mathematical aspects of quantum computing and many body physics
webpage of the project: https://nisq.pl/
Tags and Topics
Browse our collection to discover more content in these categories.
Video Information
Views
461
Likes
5
Duration
01:11:08
Published
Apr 11, 2022
Related Trending Topics
LIVE TRENDSRelated trending topics. Click any trend to explore more videos.