Unlocking Deep ReLU Networks: A Breakthrough in Fixed-Parameter Tractability 🚀
Discover how Sitan Chen's research on deep ReLU networks advances the field of parameterized complexity, making learning these models more efficient than ever. Dive into the latest insights from Frontiers of Parameterized Complexity!

Frontiers of Parameterized Complexity
470 views • Apr 15, 2021
About this video
Talks on Frontiers of Parameterized Complexity
https://frontpc.blogspot.com
Keywords: Deep ReLU Networks, FPT
March 25, 2021
Sitan Chen. Massachusetts Institute of Technology
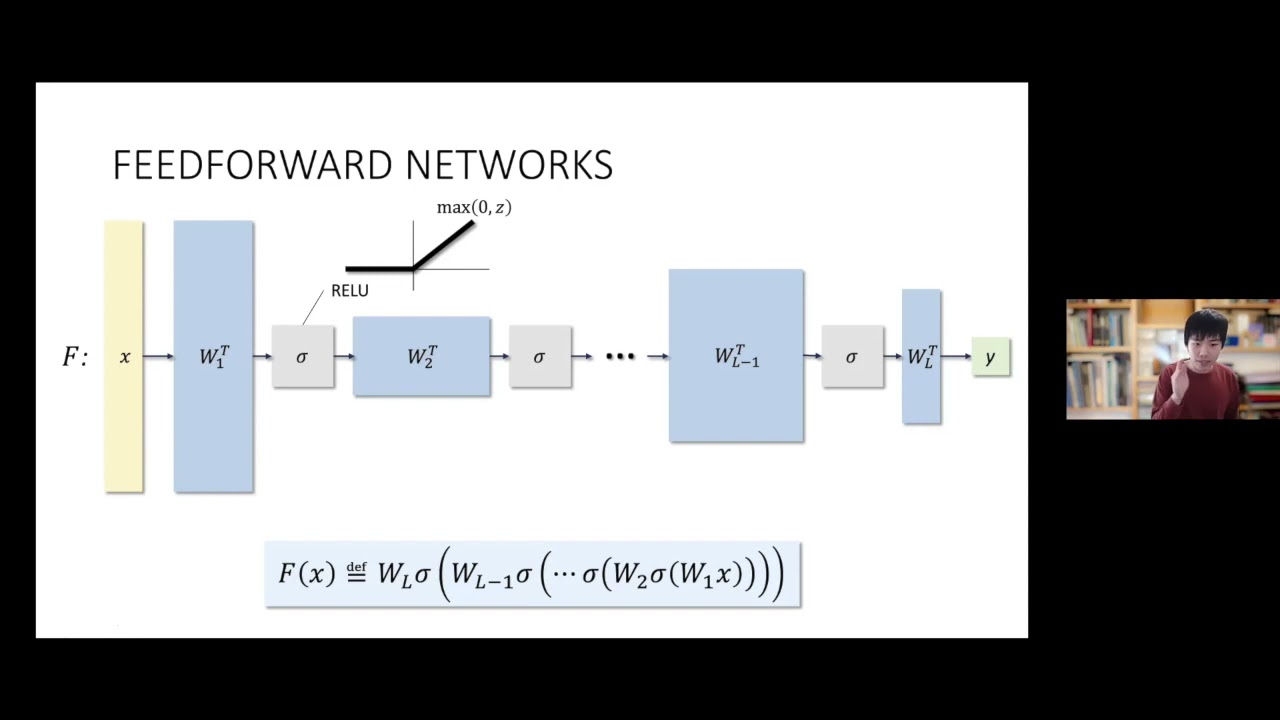
Title: Learning Deep ReLU Networks is Fixed-Parameter Tractable
Abstract: We consider the problem of learning an unknown ReLU network with an arbitrary number of layers under Gaussian inputs and obtain the first nontrivial results for networks of depth more than two. We give an algorithm whose running time is a fixed polynomial in the ambient dimension and some (exponentially large) function of only the network's parameters. These results provably cannot be obtained using gradient-based methods and give the first example of a class of efficiently learnable neural networks that gradient descent will fail to learn. In contrast, prior work for learning networks of depth three or higher requires exponential time in the ambient dimension, while prior work for the depth-two case requires well-conditioned weights and/or positive coefficients to obtain efficient run-times. Our algorithm does not require these assumptions. Our main technical tool is a type of filtered PCA that can be used to iteratively recover an approximate basis for the subspace spanned by the hidden units in the first layer. Our analysis leverages properties of lattice polynomials from tropical geometry. Based on joint work with Adam Klivans and Raghu Meka.
https://frontpc.blogspot.com
Keywords: Deep ReLU Networks, FPT
March 25, 2021
Sitan Chen. Massachusetts Institute of Technology
Title: Learning Deep ReLU Networks is Fixed-Parameter Tractable
Abstract: We consider the problem of learning an unknown ReLU network with an arbitrary number of layers under Gaussian inputs and obtain the first nontrivial results for networks of depth more than two. We give an algorithm whose running time is a fixed polynomial in the ambient dimension and some (exponentially large) function of only the network's parameters. These results provably cannot be obtained using gradient-based methods and give the first example of a class of efficiently learnable neural networks that gradient descent will fail to learn. In contrast, prior work for learning networks of depth three or higher requires exponential time in the ambient dimension, while prior work for the depth-two case requires well-conditioned weights and/or positive coefficients to obtain efficient run-times. Our algorithm does not require these assumptions. Our main technical tool is a type of filtered PCA that can be used to iteratively recover an approximate basis for the subspace spanned by the hidden units in the first layer. Our analysis leverages properties of lattice polynomials from tropical geometry. Based on joint work with Adam Klivans and Raghu Meka.
Video Information
Views
470
Likes
6
Duration
58:32
Published
Apr 15, 2021
Related Trending Topics
LIVE TRENDSRelated trending topics. Click any trend to explore more videos.