Understanding Asymmetric Cryptography: The Key to Secure Communication 🔐
Learn how asymmetric cryptography, or public-key cryptography, uses a pair of keys to ensure secure data exchange and protect your digital information effectively.

Tech Guy Greg “TG2”
40 views • Nov 23, 2023
About this video
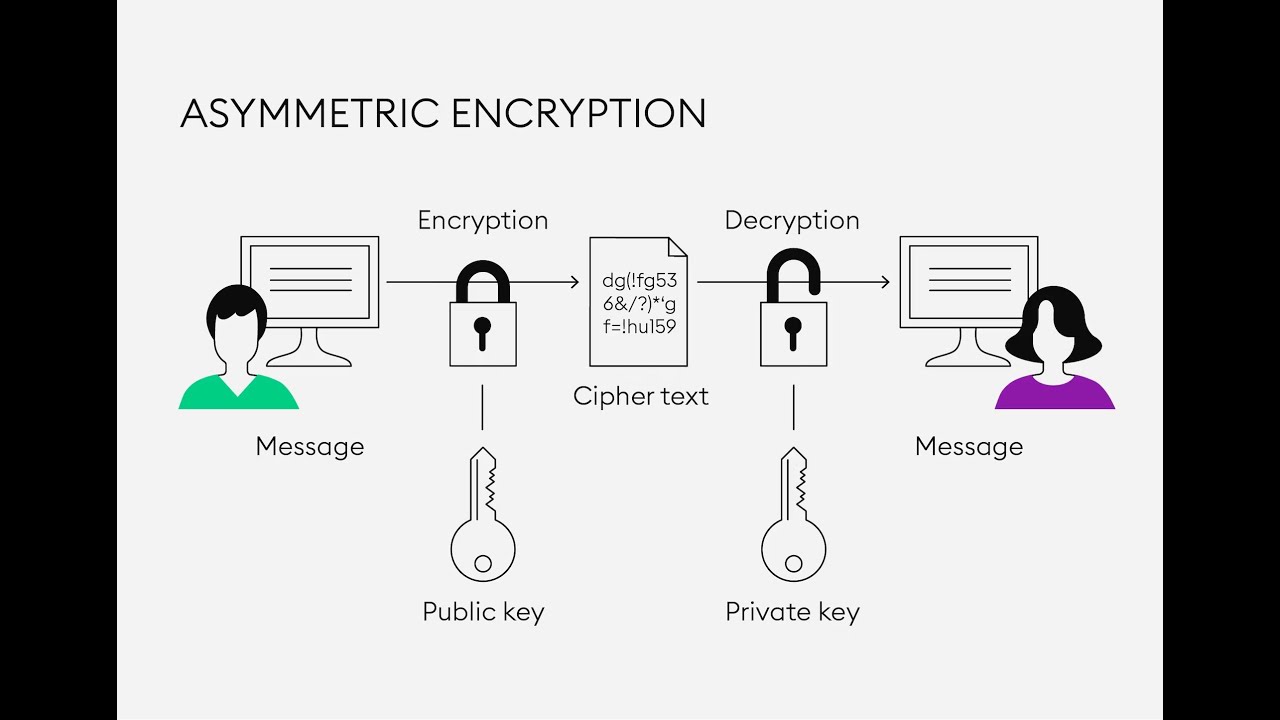
Asymmetric cryptography, also known as public-key cryptography, is a cryptographic system that uses pairs of keys: a public key and a private key. Unlike symmetric cryptography, where the same key is used for both encryption and decryption, asymmetric cryptography involves the use of two mathematically related, yet distinct, keys.
Here's an overview of how asymmetric cryptography works:
Public Key:
The public key is shared openly and can be distributed to anyone. It is used for encryption by anyone who wishes to send an encrypted message to the owner of the public key. However, the public key cannot be used to decrypt messages.
Private Key:
The private key is kept secret and known only to the owner. It is used for decrypting messages that were encrypted using the corresponding public key. The private key is never shared.
Encryption:
If person A wants to send an encrypted message to person B, A will use B's public key to encrypt the message. Once encrypted, only B, with the corresponding private key, can decrypt and read the message.
Digital Signatures:
Asymmetric cryptography is also used for creating digital signatures. The owner of a private key can use it to sign a message, providing a way for others to verify the authenticity and origin of the message using the corresponding public key.
Security and Key Exchange:
Asymmetric cryptography addresses the key exchange problem found in symmetric cryptography. In a symmetric system, if two parties want to communicate securely, they must share the same secret key. Asymmetric cryptography allows for secure communication without the need for a shared secret key.
Examples of Asymmetric Algorithms:
Common asymmetric encryption algorithms include RSA (Rivest–Shamir–Adleman), ECC (Elliptic Curve Cryptography), and DSA (Digital Signature Algorithm). These algorithms are widely used in various security protocols, including HTTPS for secure web communication.
Hybrid Cryptography:
Asymmetric cryptography is often used in conjunction with symmetric cryptography in a hybrid system. Asymmetric cryptography is used for secure key exchange, and then a symmetric key is generated for the actual encryption of the data.
Asymmetric cryptography is a fundamental component of modern secure communication systems and plays a crucial role in ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and authenticity of data in various applications, including secure communications over the internet.
Here's an overview of how asymmetric cryptography works:
Public Key:
The public key is shared openly and can be distributed to anyone. It is used for encryption by anyone who wishes to send an encrypted message to the owner of the public key. However, the public key cannot be used to decrypt messages.
Private Key:
The private key is kept secret and known only to the owner. It is used for decrypting messages that were encrypted using the corresponding public key. The private key is never shared.
Encryption:
If person A wants to send an encrypted message to person B, A will use B's public key to encrypt the message. Once encrypted, only B, with the corresponding private key, can decrypt and read the message.
Digital Signatures:
Asymmetric cryptography is also used for creating digital signatures. The owner of a private key can use it to sign a message, providing a way for others to verify the authenticity and origin of the message using the corresponding public key.
Security and Key Exchange:
Asymmetric cryptography addresses the key exchange problem found in symmetric cryptography. In a symmetric system, if two parties want to communicate securely, they must share the same secret key. Asymmetric cryptography allows for secure communication without the need for a shared secret key.
Examples of Asymmetric Algorithms:
Common asymmetric encryption algorithms include RSA (Rivest–Shamir–Adleman), ECC (Elliptic Curve Cryptography), and DSA (Digital Signature Algorithm). These algorithms are widely used in various security protocols, including HTTPS for secure web communication.
Hybrid Cryptography:
Asymmetric cryptography is often used in conjunction with symmetric cryptography in a hybrid system. Asymmetric cryptography is used for secure key exchange, and then a symmetric key is generated for the actual encryption of the data.
Asymmetric cryptography is a fundamental component of modern secure communication systems and plays a crucial role in ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and authenticity of data in various applications, including secure communications over the internet.
Video Information
Views
40
Likes
1
Duration
2:46
Published
Nov 23, 2023
Related Trending Topics
LIVE TRENDSRelated trending topics. Click any trend to explore more videos.