Big Data Ecosystem: Evolution & Future 🚀
Explore the evolution and future of the Big Data ecosystem with insights from WeWork and access the slides for deeper understanding.

Data Council
1.9K views • May 30, 2018
About this video
Get the slides: https://www.datacouncil.ai/talks/from-flat-files-to-deconstructed-database-the-evolution-and-future-of-the-big-data-ecosystem?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=social&utm_campaign=%20-%20DEC-SF-18%20Slides%20Download
ABOUT THE TALK:
Over the past ten years the Big Data infrastructure has evolved from flat files lying down in a distributed file system to a more efficient ecosystem and is turning into a fully deconstructed database.
With Hadoop, we started from a system that was good at looking for a needle in a haystack using snowplows. We had a lot of horsepower and scalability but lacked the subtlety and efficiency of relational databases.
Since Hadoop provided the ultimate flexibility compared to the more constrained and rigid RDBMSes we didn’t mind and plowed through with confidence.
Machine Learning, Recommendations, Matching, Abuse detection and in general data driven products require a more flexible infrastructure.
Over time we started applying everything that had been known to the Database world for decades to this new environment. They told us loud enough how Hadoop was a huge step backwards.
And they were right in some way. The key difference was the flexibility of it all. There are many highly integrated components in a relational database and decoupling them took some time.
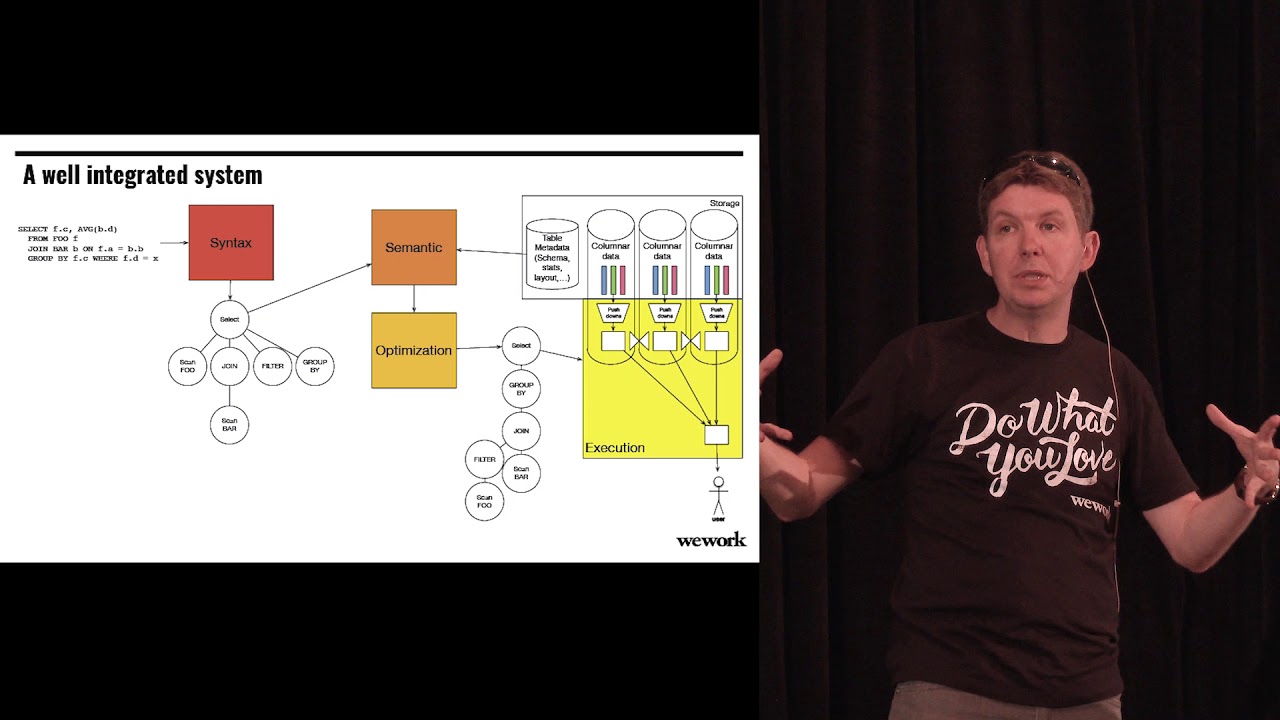
Today we see the emergence of key components (optimizer, columnar storage, in-memory representation, table abstraction, batch and streaming execution) as standards that provide the glue between the options available to process, analyze and learn from our data.
We’ve been deconstructing the tightly integrated Relational database into flexible reusable open source components. Storage, compute, multi-tenancy, batch or streaming execution are all decoupled and can be modified independently to fit every use case.
This talk will go over key open source components of the Big Data ecosystem (including Apache Calcite, Parquet, Arrow, Avro, Kafka, Batch and Streaming systems) and will describe how they all relate to each other and make our Big Data ecosystem more of a database and less of a file system. Parquet is the columnar data layout to optimize data at rest for querying. Arrow is the in-memory representation for maximum throughput execution and overhead-free data exchange. Calcite is the optimizer to make the most of our infrastructure capabilities. We’ll discuss the emerging components that are still missing or haven’t become standard yet to fully materialize the transformation to an extremely flexible database that lets you innovate with your data.
ABOUT THE SPEAKER:
Julien Le Dem is the coauthor of Apache Parquet and the PMC chair of the project. He is also a committer and PMC Member on Apache Pig, Apache Arrow and a few others. Julien is a Principal Engineer at WeWork and was previously Architect at Dremio and tech lead for Twitter’s data processing tools, where he also obtained a two-character Twitter handle (@J_). Prior to Twitter, Julien was a principal engineer and tech lead working on content platforms at Yahoo, where he received his Hadoop initiation. His French accent makes his talks particularly attractive.
ABOUT DATA COUNCIL:
Data Council (https://www.datacouncil.ai/) is a community and conference series that provides data professionals with the learning and networking opportunities they need to grow their careers. Make sure to subscribe to our channel for more videos, including DC_THURS, our series of live online interviews with leading data professionals from top open source projects and startups.
FOLLOW DATA COUNCIL:
Twitter: https://twitter.com/DataCouncilAI
LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/company/datacouncil-ai
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/datacouncilai
Eventbrite: https://www.eventbrite.com/o/data-council-30357384520
ABOUT THE TALK:
Over the past ten years the Big Data infrastructure has evolved from flat files lying down in a distributed file system to a more efficient ecosystem and is turning into a fully deconstructed database.
With Hadoop, we started from a system that was good at looking for a needle in a haystack using snowplows. We had a lot of horsepower and scalability but lacked the subtlety and efficiency of relational databases.
Since Hadoop provided the ultimate flexibility compared to the more constrained and rigid RDBMSes we didn’t mind and plowed through with confidence.
Machine Learning, Recommendations, Matching, Abuse detection and in general data driven products require a more flexible infrastructure.
Over time we started applying everything that had been known to the Database world for decades to this new environment. They told us loud enough how Hadoop was a huge step backwards.
And they were right in some way. The key difference was the flexibility of it all. There are many highly integrated components in a relational database and decoupling them took some time.
Today we see the emergence of key components (optimizer, columnar storage, in-memory representation, table abstraction, batch and streaming execution) as standards that provide the glue between the options available to process, analyze and learn from our data.
We’ve been deconstructing the tightly integrated Relational database into flexible reusable open source components. Storage, compute, multi-tenancy, batch or streaming execution are all decoupled and can be modified independently to fit every use case.
This talk will go over key open source components of the Big Data ecosystem (including Apache Calcite, Parquet, Arrow, Avro, Kafka, Batch and Streaming systems) and will describe how they all relate to each other and make our Big Data ecosystem more of a database and less of a file system. Parquet is the columnar data layout to optimize data at rest for querying. Arrow is the in-memory representation for maximum throughput execution and overhead-free data exchange. Calcite is the optimizer to make the most of our infrastructure capabilities. We’ll discuss the emerging components that are still missing or haven’t become standard yet to fully materialize the transformation to an extremely flexible database that lets you innovate with your data.
ABOUT THE SPEAKER:
Julien Le Dem is the coauthor of Apache Parquet and the PMC chair of the project. He is also a committer and PMC Member on Apache Pig, Apache Arrow and a few others. Julien is a Principal Engineer at WeWork and was previously Architect at Dremio and tech lead for Twitter’s data processing tools, where he also obtained a two-character Twitter handle (@J_). Prior to Twitter, Julien was a principal engineer and tech lead working on content platforms at Yahoo, where he received his Hadoop initiation. His French accent makes his talks particularly attractive.
ABOUT DATA COUNCIL:
Data Council (https://www.datacouncil.ai/) is a community and conference series that provides data professionals with the learning and networking opportunities they need to grow their careers. Make sure to subscribe to our channel for more videos, including DC_THURS, our series of live online interviews with leading data professionals from top open source projects and startups.
FOLLOW DATA COUNCIL:
Twitter: https://twitter.com/DataCouncilAI
LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/company/datacouncil-ai
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/datacouncilai
Eventbrite: https://www.eventbrite.com/o/data-council-30357384520
Tags and Topics
Browse our collection to discover more content in these categories.
Video Information
Views
1.9K
Likes
19
Duration
35:20
Published
May 30, 2018
User Reviews
4.2
(1) Related Trending Topics
LIVE TRENDSRelated trending topics. Click any trend to explore more videos.
Trending Now