SSL/TLS Part-1: Understanding Symmetric & Asymmetric Encryption in Hindi 🔐
Learn the basics of encryption, including how plaintext is transformed into ciphertext using symmetric and asymmetric methods. Perfect for beginners wanting to grasp SSL/TLS concepts in Hindi!

Bhairave Maulekhi
1.8K views • Dec 27, 2020
About this video
Encryption:
is the process of converting human-readable data (plaintext) into unintelligible ciphertext. This scrambling of data is the result of an algorithmic operation that uses a cryptographic key.
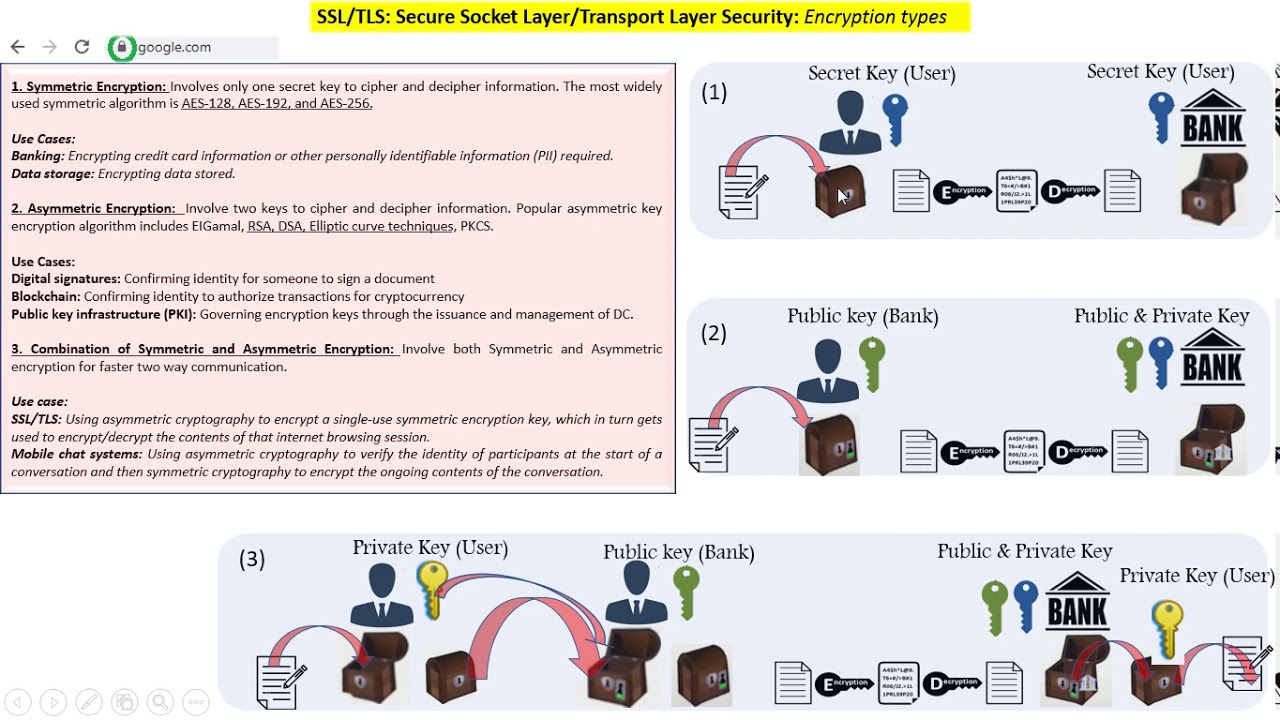
Symmetric Key Encryption:
Only one key (symmetric key) is used, and the same key is used to encrypt and decrypt the message. It’s a simple technique, and because of this, the encryption process can be carried out quickly. The length of the keys used is typically 128 or 256 bits, based on the security requirement. It’s mostly used when large chunks of data need to be transferred. The secret key is shared. Consequently, the risk of compromise is higher. Examples include RC4, AES, DES, 3DES, etc.
Asymmetric Key Encryption:
Two different cryptographic keys (asymmetric keys), called the public and the private keys, are used for encryption and decryption. It’s a much more complicated process than symmetric key encryption, and the process is slower. The length of the keys is much larger, e.g., the recommended RSA key size is 2048 bits or higher. It’s used in smaller transactions, primarily to authenticate and establish a secure communication channel prior to the actual data transfer. The private key is not shared, and the overall process is more secure as compared to symmetric encryption. Examples include RSA, Diffie-Hellman, ECC, etc.
is the process of converting human-readable data (plaintext) into unintelligible ciphertext. This scrambling of data is the result of an algorithmic operation that uses a cryptographic key.
Symmetric Key Encryption:
Only one key (symmetric key) is used, and the same key is used to encrypt and decrypt the message. It’s a simple technique, and because of this, the encryption process can be carried out quickly. The length of the keys used is typically 128 or 256 bits, based on the security requirement. It’s mostly used when large chunks of data need to be transferred. The secret key is shared. Consequently, the risk of compromise is higher. Examples include RC4, AES, DES, 3DES, etc.
Asymmetric Key Encryption:
Two different cryptographic keys (asymmetric keys), called the public and the private keys, are used for encryption and decryption. It’s a much more complicated process than symmetric key encryption, and the process is slower. The length of the keys is much larger, e.g., the recommended RSA key size is 2048 bits or higher. It’s used in smaller transactions, primarily to authenticate and establish a secure communication channel prior to the actual data transfer. The private key is not shared, and the overall process is more secure as compared to symmetric encryption. Examples include RSA, Diffie-Hellman, ECC, etc.
Tags and Topics
Browse our collection to discover more content in these categories.
Video Information
Views
1.8K
Likes
41
Duration
36:32
Published
Dec 27, 2020
User Reviews
4.5
(1) Related Trending Topics
LIVE TRENDSRelated trending topics. Click any trend to explore more videos.