Revolutionizing Image Compression: Full-Resolution Lossy Compression with Recurrent Neural Networks 📸
Discover how recurrent neural networks enable high-quality, full-resolution image compression, pushing the boundaries of efficiency and clarity in digital imaging.

ComputerVisionFoundation Videos
6.8K views • Jul 28, 2017
About this video
George Toderici, Damien Vincent, Nick Johnston, Sung Jin Hwang, David Minnen, Joel Shor, Michele Covell
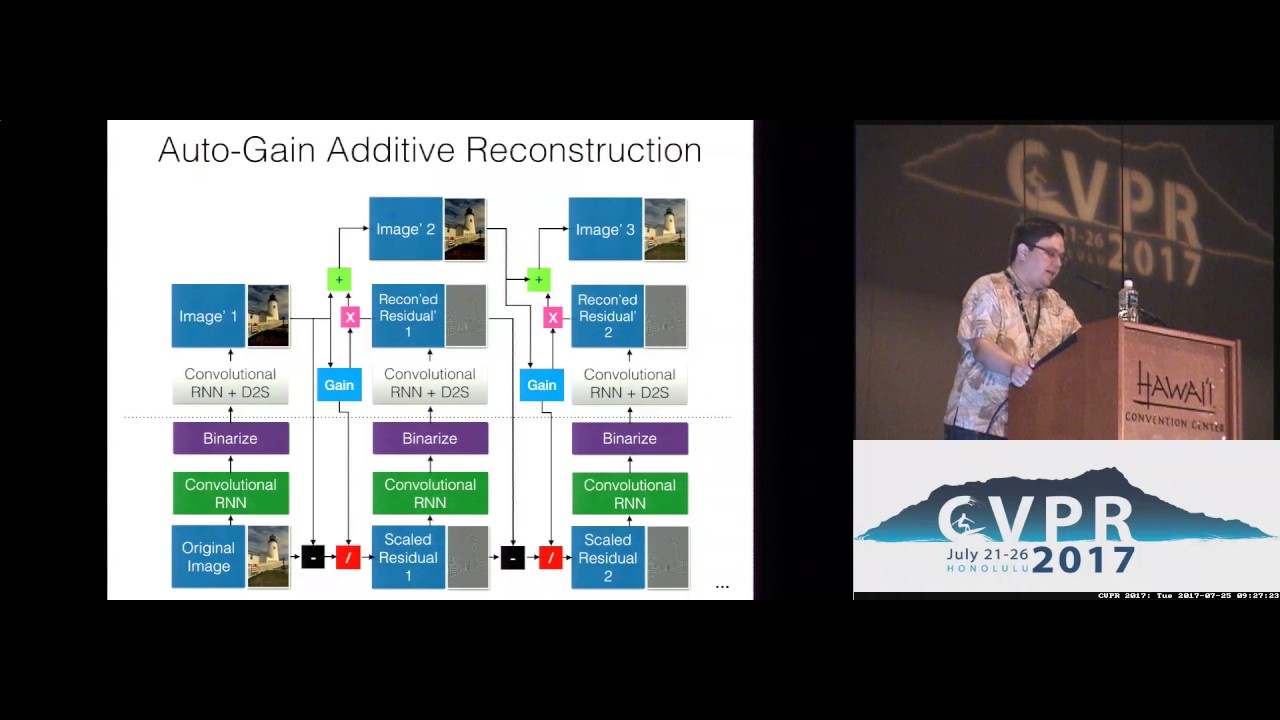
This paper presents a set of full-resolution lossy image compression methods based on neural networks. Each of the architectures we describe can provide variable compression rates during deployment without requiring retraining of the network: each network need only be trained once. All of our architectures consist of a recurrent neural network (RNN)-based encoder and decoder, a binarizer, and a neural network for entropy coding. We compare RNN types (LSTM, associative LSTM) and introduce a new hybrid of GRU and ResNet. We also study “one-shot” versus additive reconstruction architectures and introduce a new scaled-additive framework. We compare to previous work, showing improvements of 4.3%–8.8% AUC (area under the rate-distortion curve), depending on the perceptual metric used. As far as we know, this is the first neural network architecture that is able to outperform JPEG at image compression across most bitrates on the rate-distortion curve on the Kodak dataset images, with and without the aid of entropy coding.
This paper presents a set of full-resolution lossy image compression methods based on neural networks. Each of the architectures we describe can provide variable compression rates during deployment without requiring retraining of the network: each network need only be trained once. All of our architectures consist of a recurrent neural network (RNN)-based encoder and decoder, a binarizer, and a neural network for entropy coding. We compare RNN types (LSTM, associative LSTM) and introduce a new hybrid of GRU and ResNet. We also study “one-shot” versus additive reconstruction architectures and introduce a new scaled-additive framework. We compare to previous work, showing improvements of 4.3%–8.8% AUC (area under the rate-distortion curve), depending on the perceptual metric used. As far as we know, this is the first neural network architecture that is able to outperform JPEG at image compression across most bitrates on the rate-distortion curve on the Kodak dataset images, with and without the aid of entropy coding.
Tags and Topics
Browse our collection to discover more content in these categories.
Video Information
Views
6.8K
Likes
74
Duration
12:10
Published
Jul 28, 2017
User Reviews
4.3
(1) Related Trending Topics
LIVE TRENDSRelated trending topics. Click any trend to explore more videos.