Quantum Algorithms Explained: Shor's, Grover's & More | Fundamentals & Key Concepts 🔍
Dive into the world of quantum computing with this comprehensive guide covering classical vs. quantum systems, entanglement, oracles, and in-depth explanations of Shor's and Grover's algorithms. Perfect for beginners and enthusiasts alike!

Research Tech info
44 views • Jan 14, 2025
About this video
This video contains
**CLASSICAL VS QUANTUM COMPUTING**
- Classical computing uses bits, which can be either 0 or 1, processing input as a complete string of bits without hidden data.
- Quantum computing utilizes quantum bits (qubits) representing 0, 1, or both states simultaneously, allowing for more complex data processing.
- This fundamental difference enables quantum computers to perform certain computations exponentially faster than classical computers.
**QUERY MODEL OF COMPUTATION**
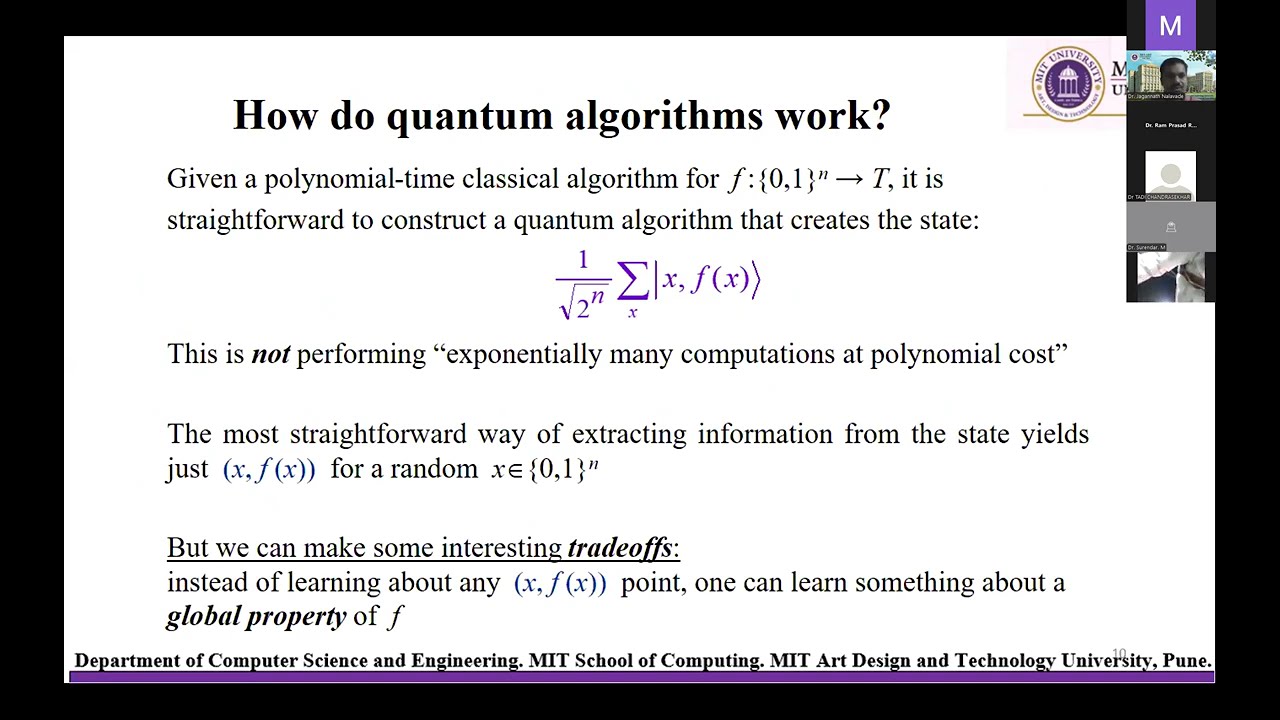
- In the query model, inputs are processed as queries rather than direct bit strings, introducing the concept of an Oracle, or black box, which operates on input queries and returns outputs without revealing its internal workings.
- The efficiency of a quantum algorithm in this model is determined by the number of queries required to achieve a result, which can be significantly lower than in classical computations.
- Typical problems addressed include identifying specific strings among inputs, determining parity, and finding minimum values.
**INTRODUCTION TO QUANTUM ALGORITHMS**
- Quantum algorithms like the Deutsch algorithm demonstrate how quantum computing can outperform classical approaches in solving problems related to function evaluation.
- The Deutsch problem differentiates between constant and balanced functions, showcasing the ability of quantum algorithms to solve problems with fewer queries.
- The efficiency of quantum algorithms is often tied to their ability to create superpositions and entangled states, enhancing computational speed.
**SHOR'S ALGORITHM FOR FACTORING**
- Shor's algorithm is a significant quantum algorithm that factors large integers in polynomial time, which is infeasible for classical computers.
- The algorithm relies on quantum parallelism and the Quantum Fourier Transform to identify periodicities in modular arithmetic.
- Its implications are profound for cryptography, as it can potentially break widely used encryption systems based on the difficulty of factoring large numbers.
**GROVER'S ALGORITHM FOR UNSEARCHED DATABASES**
- Grover's algorithm provides a quadratic speedup for searching unsorted databases, needing only √N steps to find an item in a database of N items.
- This algorithm exemplifies the power of quantum computing in efficiently solving search problems compared to classical algorithms, which may require linear time.
- Applications include searching databases, optimizing routes, and identifying patterns, making Grover's algorithm a versatile tool in quantum computing.
**SIMON'S ALGORITHM AND ITS APPLICATIONS**
- Simon's algorithm addresses functions with a hidden string, focusing on identifying whether a function is one-to-one or two-to-one, demonstrating quantum advantage in specific problem-solving scenarios.
- The algorithm utilizes a series of quantum operations and measurements to extract the hidden information efficiently.
- Its inclusion in the quantum algorithm toolkit highlights the diverse applications of quantum computing in solving complex computational problems.
**PRACTICAL IMPLEMENTATIONS OF QUANTUM COMPUTING**
- Leading companies like IBM, Microsoft, and Google are at the forefront of quantum computing research, developing hardware, software, and quantum programming languages.
- IBM's Q Series and Microsoft's Q# language exemplify ongoing efforts to create practical quantum systems and applications.
- The ongoing evolution of quantum algorithms promises advancements in fields ranging from cryptography to optimization, paving the way for future technological breakthroughs.
Introduction and History of Quantum Computing
Data Representation
Operations on Data
Shor's Algorithm
Deutsch's Problem
Simon's Algorithm
Grover's Algorithm
**CLASSICAL VS QUANTUM COMPUTING**
- Classical computing uses bits, which can be either 0 or 1, processing input as a complete string of bits without hidden data.
- Quantum computing utilizes quantum bits (qubits) representing 0, 1, or both states simultaneously, allowing for more complex data processing.
- This fundamental difference enables quantum computers to perform certain computations exponentially faster than classical computers.
**QUERY MODEL OF COMPUTATION**
- In the query model, inputs are processed as queries rather than direct bit strings, introducing the concept of an Oracle, or black box, which operates on input queries and returns outputs without revealing its internal workings.
- The efficiency of a quantum algorithm in this model is determined by the number of queries required to achieve a result, which can be significantly lower than in classical computations.
- Typical problems addressed include identifying specific strings among inputs, determining parity, and finding minimum values.
**INTRODUCTION TO QUANTUM ALGORITHMS**
- Quantum algorithms like the Deutsch algorithm demonstrate how quantum computing can outperform classical approaches in solving problems related to function evaluation.
- The Deutsch problem differentiates between constant and balanced functions, showcasing the ability of quantum algorithms to solve problems with fewer queries.
- The efficiency of quantum algorithms is often tied to their ability to create superpositions and entangled states, enhancing computational speed.
**SHOR'S ALGORITHM FOR FACTORING**
- Shor's algorithm is a significant quantum algorithm that factors large integers in polynomial time, which is infeasible for classical computers.
- The algorithm relies on quantum parallelism and the Quantum Fourier Transform to identify periodicities in modular arithmetic.
- Its implications are profound for cryptography, as it can potentially break widely used encryption systems based on the difficulty of factoring large numbers.
**GROVER'S ALGORITHM FOR UNSEARCHED DATABASES**
- Grover's algorithm provides a quadratic speedup for searching unsorted databases, needing only √N steps to find an item in a database of N items.
- This algorithm exemplifies the power of quantum computing in efficiently solving search problems compared to classical algorithms, which may require linear time.
- Applications include searching databases, optimizing routes, and identifying patterns, making Grover's algorithm a versatile tool in quantum computing.
**SIMON'S ALGORITHM AND ITS APPLICATIONS**
- Simon's algorithm addresses functions with a hidden string, focusing on identifying whether a function is one-to-one or two-to-one, demonstrating quantum advantage in specific problem-solving scenarios.
- The algorithm utilizes a series of quantum operations and measurements to extract the hidden information efficiently.
- Its inclusion in the quantum algorithm toolkit highlights the diverse applications of quantum computing in solving complex computational problems.
**PRACTICAL IMPLEMENTATIONS OF QUANTUM COMPUTING**
- Leading companies like IBM, Microsoft, and Google are at the forefront of quantum computing research, developing hardware, software, and quantum programming languages.
- IBM's Q Series and Microsoft's Q# language exemplify ongoing efforts to create practical quantum systems and applications.
- The ongoing evolution of quantum algorithms promises advancements in fields ranging from cryptography to optimization, paving the way for future technological breakthroughs.
Introduction and History of Quantum Computing
Data Representation
Operations on Data
Shor's Algorithm
Deutsch's Problem
Simon's Algorithm
Grover's Algorithm
Tags and Topics
Browse our collection to discover more content in these categories.
Video Information
Views
44
Duration
01:46:54
Published
Jan 14, 2025
Related Trending Topics
LIVE TRENDSRelated trending topics. Click any trend to explore more videos.