Master the Circular Queue in Data Structures 🌀
Learn how a Circular Queue enhances traditional queues by connecting ends to optimize space and efficiency. Perfect for understanding advanced data structure concepts!

Apna Engineer
56.7K views • Jan 16, 2025
About this video
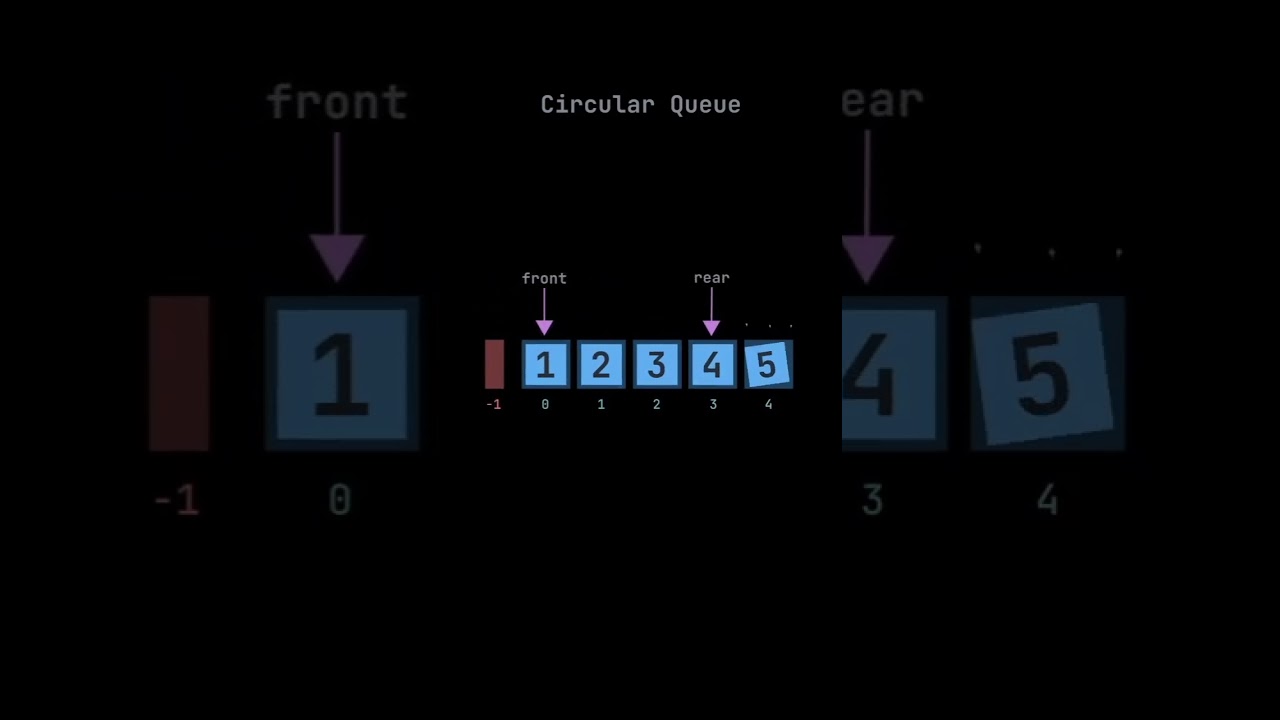
A Circular Queue is a data structure that overcomes the limitations of a regular queue by connecting the ends of the queue to form a circle. This allows for efficient use of memory by reusing the empty spaces left behind after dequeuing elements. It is implemented using arrays or linked lists and works in a FIFO (First In First Out) manner.
Key Features:
1. Circular Arrangement: The last position is connected to the first position to form a circle.
2. Efficient Space Utilization: It uses all available slots, avoiding the issue of wasted space in a linear queue.
3. Front and Rear Pointers:
Front: Points to the first element in the queue.
Rear: Points to the last element in the queue.
Operations:
1. Enqueue (Insert):
Add an element to the rear of the queue.
Check if the queue is full before inserting.
Update the rear pointer circularly ((rear + 1) % size).
2. Dequeue (Delete):
Remove an element from the front of the queue.
Check if the queue is empty before removing.
Update the front pointer circularly ((front + 1) % size).
3. Peek:
Retrieve the front element without removing it.
4. IsFull:
Check if the queue is full ((rear + 1) % size == front).
5. IsEmpty:
Check if the queue is empty (front == -1).
---
Implementation (Array-based Circular Queue in Python):
class CircularQueue:
def __init__(self, size):
self.size = size
self.queue = [None] * size
self.front = -1
self.rear = -1
def enqueue(self, data):
if (self.rear + 1) % self.size == self.front:
print("Queue is Full")
else:
if self.front == -1: # First insertion
self.front = 0
self.rear = (self.rear + 1) % self.size
self.queue[self.rear] = data
print(f"Enqueued: {data}")
def dequeue(self):
if self.front == -1:
print("Queue is Empty")
else:
removed = self.queue[self.front]
if self.front == self.rear: # Queue becomes empty
self.front = self.rear = -1
else:
self.front = (self.front + 1) % self.size
print(f"Dequeued: {removed}")
def display(self):
if self.front == -1:
print("Queue is Empty")
else:
index = self.front
print("Queue elements:", end=" ")
while True:
print(self.queue[index], end=" ")
if index == self.rear:
break
index = (index + 1) % self.size
print()
# Example Usage
cq = CircularQueue(5)
cq.enqueue(10)
cq.enqueue(20)
cq.enqueue(30)
cq.display()
cq.dequeue()
cq.display()
cq.enqueue(40)
cq.enqueue(50)
cq.enqueue(60) # Queue is Full
cq.display()
This code implements the Circular Queue with operations like enqueue, dequeue, and display.
Key Features:
1. Circular Arrangement: The last position is connected to the first position to form a circle.
2. Efficient Space Utilization: It uses all available slots, avoiding the issue of wasted space in a linear queue.
3. Front and Rear Pointers:
Front: Points to the first element in the queue.
Rear: Points to the last element in the queue.
Operations:
1. Enqueue (Insert):
Add an element to the rear of the queue.
Check if the queue is full before inserting.
Update the rear pointer circularly ((rear + 1) % size).
2. Dequeue (Delete):
Remove an element from the front of the queue.
Check if the queue is empty before removing.
Update the front pointer circularly ((front + 1) % size).
3. Peek:
Retrieve the front element without removing it.
4. IsFull:
Check if the queue is full ((rear + 1) % size == front).
5. IsEmpty:
Check if the queue is empty (front == -1).
---
Implementation (Array-based Circular Queue in Python):
class CircularQueue:
def __init__(self, size):
self.size = size
self.queue = [None] * size
self.front = -1
self.rear = -1
def enqueue(self, data):
if (self.rear + 1) % self.size == self.front:
print("Queue is Full")
else:
if self.front == -1: # First insertion
self.front = 0
self.rear = (self.rear + 1) % self.size
self.queue[self.rear] = data
print(f"Enqueued: {data}")
def dequeue(self):
if self.front == -1:
print("Queue is Empty")
else:
removed = self.queue[self.front]
if self.front == self.rear: # Queue becomes empty
self.front = self.rear = -1
else:
self.front = (self.front + 1) % self.size
print(f"Dequeued: {removed}")
def display(self):
if self.front == -1:
print("Queue is Empty")
else:
index = self.front
print("Queue elements:", end=" ")
while True:
print(self.queue[index], end=" ")
if index == self.rear:
break
index = (index + 1) % self.size
print()
# Example Usage
cq = CircularQueue(5)
cq.enqueue(10)
cq.enqueue(20)
cq.enqueue(30)
cq.display()
cq.dequeue()
cq.display()
cq.enqueue(40)
cq.enqueue(50)
cq.enqueue(60) # Queue is Full
cq.display()
This code implements the Circular Queue with operations like enqueue, dequeue, and display.
Video Information
Views
56.7K
Duration
0:09
Published
Jan 16, 2025
User Reviews
3.9
(11) Related Trending Topics
LIVE TRENDSRelated trending topics. Click any trend to explore more videos.
Trending Now