Master Polynomial-Time Reductions in Computability & Complexity Theory 🔍
Discover the essentials of Polynomial-Time Reductions and how they relate problems in Computability and Complexity Theory. Perfect for understanding problem transformations and complexity classes!

Advanced Maths
74 views • Oct 27, 2025
About this video
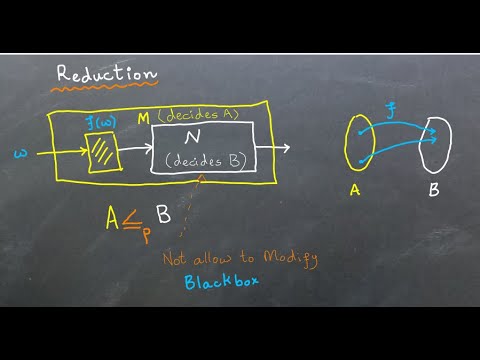
In this video, we revisit the concept of Polynomial-Time Reduction, a fundamental idea in Computability and Complexity Theory.
You’ll learn how one problem (language A) can be transformed into another problem (language B) using a polynomial-time computable function f, without ever looking inside the machine that solves B.
We go through the formal definition from Sipser’s textbook, explain the intuition behind reductions, and show how transitivity of reductions helps us understand the structure of computational problems — a key step toward understanding NP-completeness.
To make it concrete, we discuss an example involving graph problems, where the longest path problem in a DAG is reduced to the shortest path problem by simply negating edge weights. This example illustrates how reductions connect problems and why the notion of polynomial-time computation matters.
Topics Covered:
* Definition of polynomial-time reduction (A ≤p B)
* Using one Turing machine as a black box for another
* Transitivity of reductions
* Example: Reducing longest path to shortest path in a DAG
* Relevance to NP-complete problems
You’ll learn how one problem (language A) can be transformed into another problem (language B) using a polynomial-time computable function f, without ever looking inside the machine that solves B.
We go through the formal definition from Sipser’s textbook, explain the intuition behind reductions, and show how transitivity of reductions helps us understand the structure of computational problems — a key step toward understanding NP-completeness.
To make it concrete, we discuss an example involving graph problems, where the longest path problem in a DAG is reduced to the shortest path problem by simply negating edge weights. This example illustrates how reductions connect problems and why the notion of polynomial-time computation matters.
Topics Covered:
* Definition of polynomial-time reduction (A ≤p B)
* Using one Turing machine as a black box for another
* Transitivity of reductions
* Example: Reducing longest path to shortest path in a DAG
* Relevance to NP-complete problems
Tags and Topics
Browse our collection to discover more content in these categories.
Video Information
Views
74
Likes
5
Duration
6:20
Published
Oct 27, 2025
Related Trending Topics
LIVE TRENDSRelated trending topics. Click any trend to explore more videos.