Introduction to Analytic Geometry: Lesson 1
This lesson introduces the fundamentals of analytic geometry, highlighting the contributions of Rene Descartes, the Father of Modern Philosophy. It covers the notation of exponents as superscripts of variables.
Punjab Group of Colleges
26 views • May 5, 2015
About this video
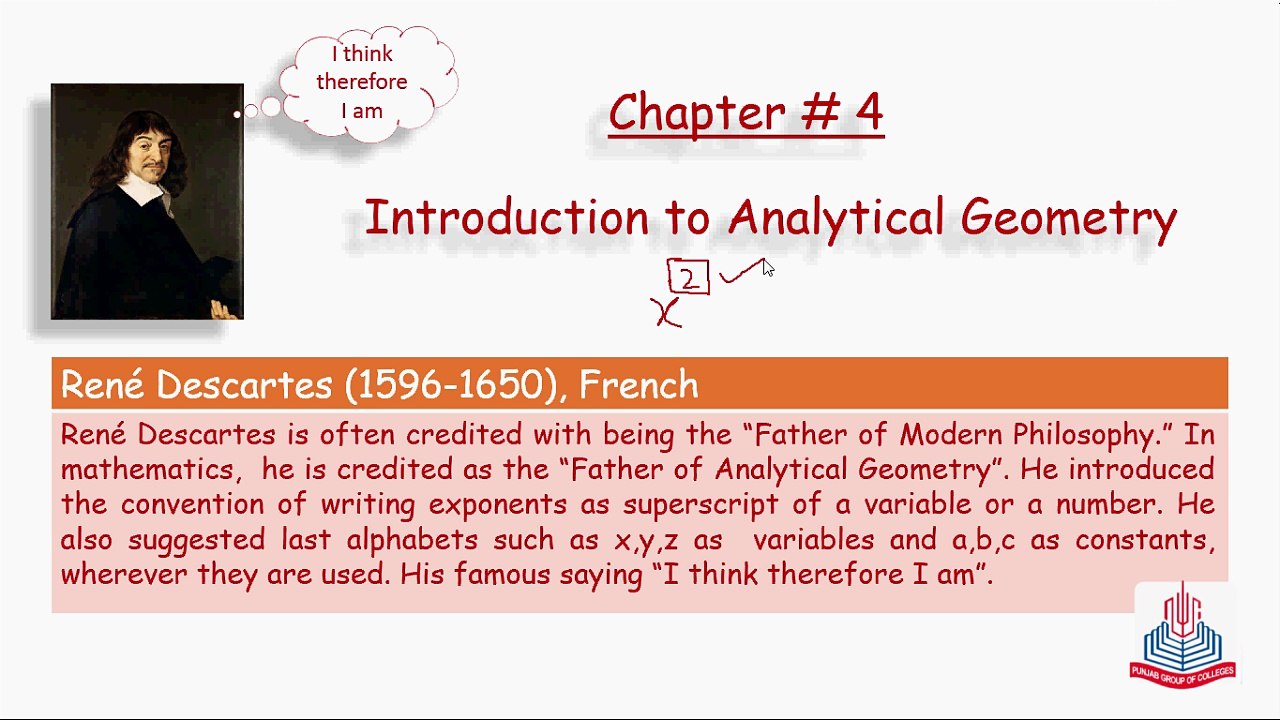
Lesson#1 <br />Introduction to Analytical Geometry <br />Rene Descartes (1596-1650), French, (Father of Modern Philosophy) <br />Writing exponents as superscript of a variable or a number. <br />x,y,z as variable <br />a,b,c as constants. <br />"I think therefore I am" <br />PROBLEMS CAN BE SOLVED BY FINDING <br />* Distance between two points. <br />* Distance between a point and a line. <br />* Any point between two points. <br />* Mid point of two points. <br />* Examining polygons and their properties. <br />* Equation of a straight line. <br />* Inclination of a line. <br />* Slope of a given line. <br />* Slopes of parallel lines as well as perpendicular lines, and their relationships. <br />WHAT IS GEOMETRY AND WHAT IS ANALYTICAL GEOMETRY? <br />1. Word Geometry is derived from two greek words GEO (meaning earth) and METRON (meaning measurement). <br />2. Analytical geometry is the fusion of algebra and geometry. <br />chapter No 4 <br />Introduction to Analytical Geometry <br />Exercise No 4.1
Video Information
Views
26
Duration
7:36
Published
May 5, 2015
Related Trending Topics
LIVE TRENDSRelated trending topics. Click any trend to explore more videos.