Master Silicate Types with Easy Tricks | IIT JEE & NEET Preparation 😊
Learn simple methods to identify and classify silicates for IIT JEE, NEET, and other exams. Boost your chemistry skills with our expert tips and tricks!

One Chemistry
252 views • Jul 24, 2025
About this video
For feedback and business queries, please email us at suviganu@gmail.com
Silicates are a group of chemical compounds made mostly of silicon (Si), oxygen (O), and sometimes other elements like aluminum, iron, calcium, or magnesium.
Silicates are the most common minerals on Earth.
They make up over 90% of the Earth's crust!
Found in rocks, soil, sand, clay, and many building materials.
Basic Unit: The Silicate Tetrahedron
The smallest part of a silicate is called a silicate tetrahedron.
It has one silicon atom in the center and four oxygen atoms at the corners.
Its chemical formula is SiO₄⁴⁻.
These tetrahedra can stay separate or join together in different ways.
Silicates are not just found in rocks — they’re also used in:
Glass and ceramics
Cement and concrete
Electronics and optical fibers
Even in makeup and toothpaste
Their properties (like hardness, color, and resistance to heat) come from how their tetrahedra are connected.
Let’s look at the different types of silicates based on how the tetrahedra are joined.
Types of silicates
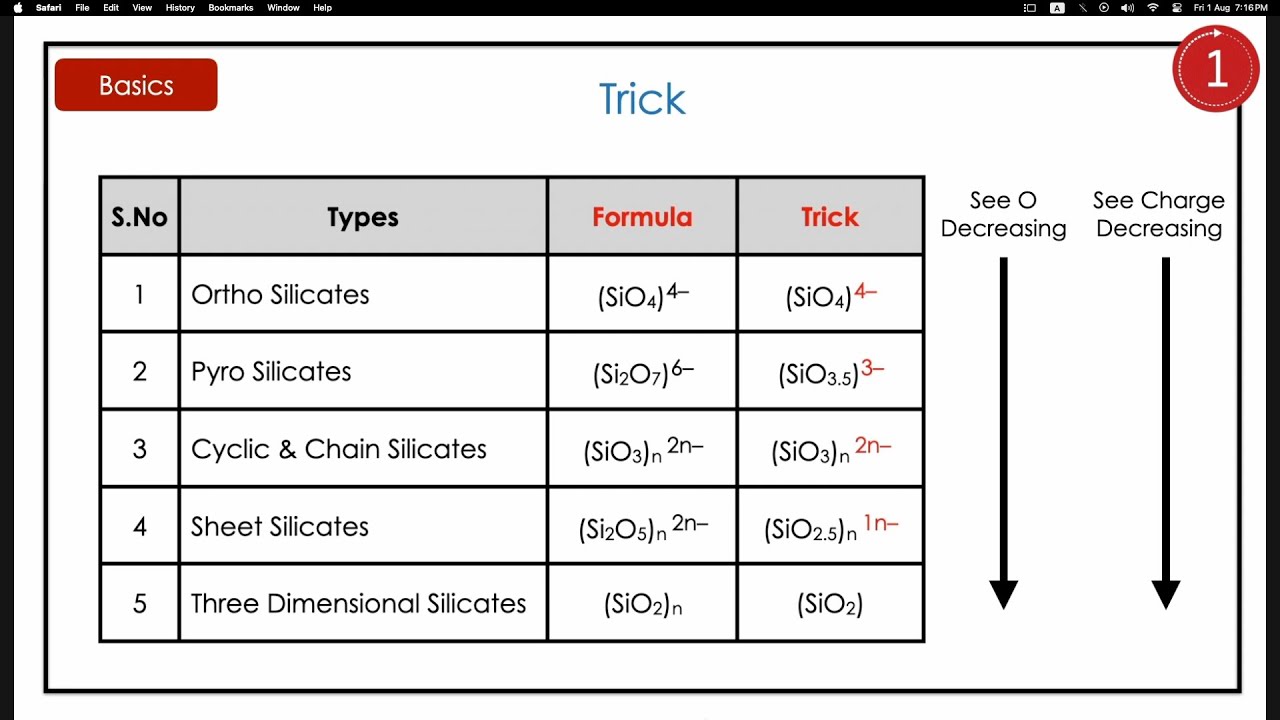
1. Orthosilicates (Nesosilicates)
Tetrahedra are not connected to each other.
Each tetrahedron is isolated.
General formula: SiO₄⁴⁻
Example: Olivine
Use: Found in igneous rocks
2. Pyrosilicates (Sorosilicates)
Two tetrahedra share one oxygen atom.
General formula: Si₂O₇⁶⁻
Example: Hemimorphite
Use: In zinc ores
3. Cyclosilicates (Ring Silicates)
Tetrahedra join to form rings.
Common ring sizes: 3, 4, or 6 tetrahedra.
General formula (for 6-membered ring): Si₆O₁₈¹²⁻
Example: Beryl (contains emerald and aquamarine)
Use: Gemstones
Page 4: More Types of Silicates
4. Inosilicates (Chain Silicates)
Tetrahedra link to form chains.
a) Single Chain
General formula: (SiO₃)ⁿ²ⁿ⁻
Example: Pyroxenes
Use: Found in volcanic rocks
b) Double Chain
Two single chains join side by side.
General formula: (Si₄O₁₁)ⁿ⁶ⁿ⁻
Example: Amphiboles
Use: In asbestos minerals
5. Phyllosilicates (Sheet Silicates)
Tetrahedra form flat sheets, each sharing three oxygen atoms.
General formula: (Si₂O₅)ⁿ²ⁿ⁻
Examples: Mica, Talc, Clay minerals
Use: In makeup, ceramics, and insulation
6. Tectosilicates (Framework Silicates)
All four oxygen atoms are shared between tetrahedra.
Forms a 3D framework.
General formula: SiO₂ (for pure silica)
Examples: Quartz, Feldspar, Zeolites
Use: In glass, granite, and water softeners
Quick Summary Table
Type Structure Formula Example Common Use
Orthosilicate Isolated SiO₄⁴⁻ Rock-forming minerals
Pyrosilicate 2 Tetrahedra Si₂O₇⁶⁻ Zinc ores
Cyclosilicate Ring Si₆O₁₈¹²⁻ Gemstones
Inosilicate Chain SiO₃²⁻ / Si₄O₁₁⁶⁻ Volcanic rocks, Asbestos
Phyllosilicate Sheet Si₂O₅²⁻ Talc, Mica, Clay
Tectosilicate Framework SiO₂ Quartz, Glass, Ceramics
The video may contain
What is Orthosilicate
What is Pyrosilicate
What is Cyclosilicate Ring
What is Inosilicate Chain
What is Phyllosilicate
What is Tectosilicate Framework
General formula for silicates
How to find silicates
What are the other names of silicates
How to identify the silicates
video is Ideal for Chemistry Exams
Competitive Exams Like
GATE Chemistry
NET Chemical Science
UGC Chemical Science
SET Chemistry
JEE Chemistry
JAM Chemistry
NEET Chemistry
#OrganicChemistry
#ChemistryExplained
#ChemicalReactions
#LearnChemistry
#MolecularScience
#ChemistryTutorials
#ScienceExperiments
#InorganicChemistry
#PhysicalChemistry
#ChemistryFacts
#OrganicReactions
#ReactionMechanism
#ChemistryMechanisms
#AdvancedOrganicChemistry
#ChemistryExamPrep
#CompetitiveChemistry
#ChemistryMCQs
#JEEChemistry
#NEETChemistry
#ChemistryRevision
#PhysicalChemistryTricks
#OrganicChemistryShortcuts
#ChemistryStudyTips
#competitiveexampreparation #netchemistry #gatechemistry
Silicates are a group of chemical compounds made mostly of silicon (Si), oxygen (O), and sometimes other elements like aluminum, iron, calcium, or magnesium.
Silicates are the most common minerals on Earth.
They make up over 90% of the Earth's crust!
Found in rocks, soil, sand, clay, and many building materials.
Basic Unit: The Silicate Tetrahedron
The smallest part of a silicate is called a silicate tetrahedron.
It has one silicon atom in the center and four oxygen atoms at the corners.
Its chemical formula is SiO₄⁴⁻.
These tetrahedra can stay separate or join together in different ways.
Silicates are not just found in rocks — they’re also used in:
Glass and ceramics
Cement and concrete
Electronics and optical fibers
Even in makeup and toothpaste
Their properties (like hardness, color, and resistance to heat) come from how their tetrahedra are connected.
Let’s look at the different types of silicates based on how the tetrahedra are joined.
Types of silicates
1. Orthosilicates (Nesosilicates)
Tetrahedra are not connected to each other.
Each tetrahedron is isolated.
General formula: SiO₄⁴⁻
Example: Olivine
Use: Found in igneous rocks
2. Pyrosilicates (Sorosilicates)
Two tetrahedra share one oxygen atom.
General formula: Si₂O₇⁶⁻
Example: Hemimorphite
Use: In zinc ores
3. Cyclosilicates (Ring Silicates)
Tetrahedra join to form rings.
Common ring sizes: 3, 4, or 6 tetrahedra.
General formula (for 6-membered ring): Si₆O₁₈¹²⁻
Example: Beryl (contains emerald and aquamarine)
Use: Gemstones
Page 4: More Types of Silicates
4. Inosilicates (Chain Silicates)
Tetrahedra link to form chains.
a) Single Chain
General formula: (SiO₃)ⁿ²ⁿ⁻
Example: Pyroxenes
Use: Found in volcanic rocks
b) Double Chain
Two single chains join side by side.
General formula: (Si₄O₁₁)ⁿ⁶ⁿ⁻
Example: Amphiboles
Use: In asbestos minerals
5. Phyllosilicates (Sheet Silicates)
Tetrahedra form flat sheets, each sharing three oxygen atoms.
General formula: (Si₂O₅)ⁿ²ⁿ⁻
Examples: Mica, Talc, Clay minerals
Use: In makeup, ceramics, and insulation
6. Tectosilicates (Framework Silicates)
All four oxygen atoms are shared between tetrahedra.
Forms a 3D framework.
General formula: SiO₂ (for pure silica)
Examples: Quartz, Feldspar, Zeolites
Use: In glass, granite, and water softeners
Quick Summary Table
Type Structure Formula Example Common Use
Orthosilicate Isolated SiO₄⁴⁻ Rock-forming minerals
Pyrosilicate 2 Tetrahedra Si₂O₇⁶⁻ Zinc ores
Cyclosilicate Ring Si₆O₁₈¹²⁻ Gemstones
Inosilicate Chain SiO₃²⁻ / Si₄O₁₁⁶⁻ Volcanic rocks, Asbestos
Phyllosilicate Sheet Si₂O₅²⁻ Talc, Mica, Clay
Tectosilicate Framework SiO₂ Quartz, Glass, Ceramics
The video may contain
What is Orthosilicate
What is Pyrosilicate
What is Cyclosilicate Ring
What is Inosilicate Chain
What is Phyllosilicate
What is Tectosilicate Framework
General formula for silicates
How to find silicates
What are the other names of silicates
How to identify the silicates
video is Ideal for Chemistry Exams
Competitive Exams Like
GATE Chemistry
NET Chemical Science
UGC Chemical Science
SET Chemistry
JEE Chemistry
JAM Chemistry
NEET Chemistry
#OrganicChemistry
#ChemistryExplained
#ChemicalReactions
#LearnChemistry
#MolecularScience
#ChemistryTutorials
#ScienceExperiments
#InorganicChemistry
#PhysicalChemistry
#ChemistryFacts
#OrganicReactions
#ReactionMechanism
#ChemistryMechanisms
#AdvancedOrganicChemistry
#ChemistryExamPrep
#CompetitiveChemistry
#ChemistryMCQs
#JEEChemistry
#NEETChemistry
#ChemistryRevision
#PhysicalChemistryTricks
#OrganicChemistryShortcuts
#ChemistryStudyTips
#competitiveexampreparation #netchemistry #gatechemistry
Video Information
Views
252
Likes
11
Duration
11:28
Published
Jul 24, 2025
Related Trending Topics
LIVE TRENDSRelated trending topics. Click any trend to explore more videos.
Trending Now