Efficient Classic McEliece Implementation for Embedded Devices 🔒
Discover how to implement the classic McEliece cryptosystem with a low memory footprint, optimized for embedded systems. Watch the presentation based on the Springer paper for insights and practical techniques.

MTG AG – Enterprise Resource Security
336 views • Apr 12, 2021
About this video
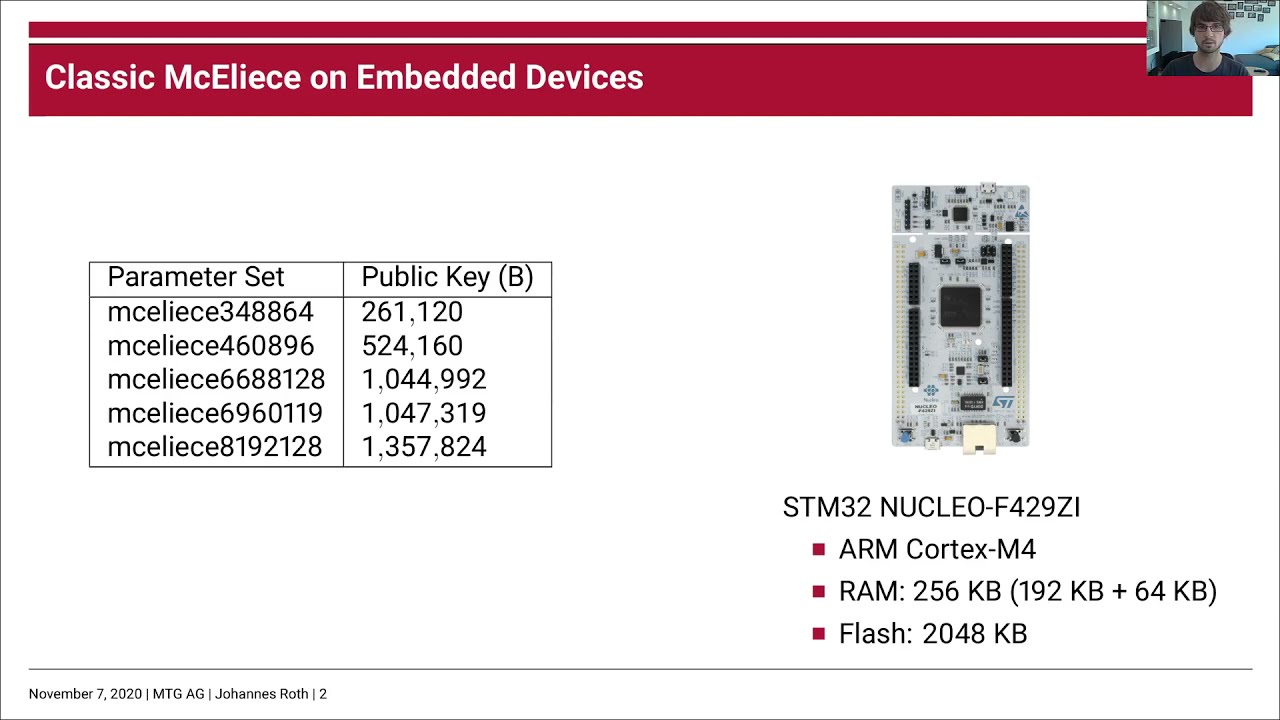
Classic McEliece on Embedded Devices
This is a video presentation for the paper Classic McEliece Implementation with Low Memory Footprint ([Springer](https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-030-68487-7_3) | [ePrint](https://eprint.iacr.org/2021/138).
The Classic McEliece cryptosystem is one of the most trusted quantum-resistant cryptographic schemes.
Deploying it in practical applications, however, is challenging due to the size of its public key.
In this work, we bridge this gap.
We present an implementation of Classic McEliece on an ARM Cortex-M4 processor, optimized to overcome memory constraints.
To this end, we present an algorithm to retrieve the public key ad-hoc.
This reduces memory and storage requirements and enables the generation of larger key pairs on the device.
To further improve the implementation, we perform the public key operation by streaming the key to avoid storing it as a whole.
This additionally reduces the risk of denial of service attacks.
Finally, we use these results to implement and run TLS on the embedded device
This is a video presentation for the paper Classic McEliece Implementation with Low Memory Footprint ([Springer](https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-030-68487-7_3) | [ePrint](https://eprint.iacr.org/2021/138).
The Classic McEliece cryptosystem is one of the most trusted quantum-resistant cryptographic schemes.
Deploying it in practical applications, however, is challenging due to the size of its public key.
In this work, we bridge this gap.
We present an implementation of Classic McEliece on an ARM Cortex-M4 processor, optimized to overcome memory constraints.
To this end, we present an algorithm to retrieve the public key ad-hoc.
This reduces memory and storage requirements and enables the generation of larger key pairs on the device.
To further improve the implementation, we perform the public key operation by streaming the key to avoid storing it as a whole.
This additionally reduces the risk of denial of service attacks.
Finally, we use these results to implement and run TLS on the embedded device
Tags and Topics
Browse our collection to discover more content in these categories.
Video Information
Views
336
Likes
5
Duration
24:51
Published
Apr 12, 2021
Related Trending Topics
LIVE TRENDSRelated trending topics. Click any trend to explore more videos.
Trending Now