COMP 1672: Mastering Steganography – Encoding Secrets & Key Methods 🔐
Learn how to encode secret messages, handle exceptions, and implement getDataLocations methods in this comprehensive guide to Steganography for COMP 1672. Perfect for beginners and coding enthusiasts!

Evan Derby
874 views • Feb 22, 2017
About this video
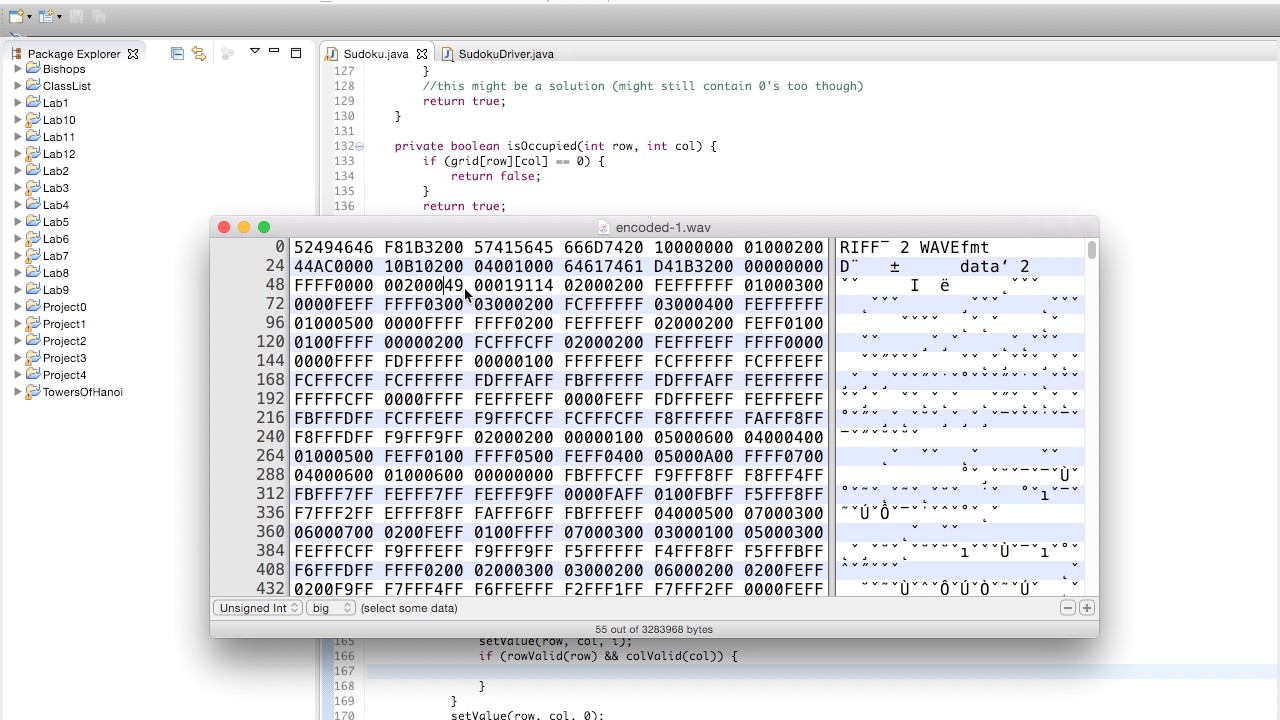
In this video I take you through how a secret message is encoded, how to write the two required exceptions, and how to write the getDataLocations methods.
CORRECTION:
At 6:10, I state that Java's primitive integer type is unsigned. This is incorrect. All primitive number types in Java are signed. However, it wouldn't have mattered if I used the signed or unsigned options in my hexadecimal editor, because short messages like the ones encrypted with the steganography program aren't likely to be long enough and have enough characters to overflow the signed integer value. Numbers between 0 and +2,147,483,647 (the maximum value of a 4-byte/32-bit signed integer in Java) will be displayed the same, whether we choose Unsigned Integer or Signed Integer.
CORRECTION:
At 6:10, I state that Java's primitive integer type is unsigned. This is incorrect. All primitive number types in Java are signed. However, it wouldn't have mattered if I used the signed or unsigned options in my hexadecimal editor, because short messages like the ones encrypted with the steganography program aren't likely to be long enough and have enough characters to overflow the signed integer value. Numbers between 0 and +2,147,483,647 (the maximum value of a 4-byte/32-bit signed integer in Java) will be displayed the same, whether we choose Unsigned Integer or Signed Integer.
Tags and Topics
Browse our collection to discover more content in these categories.
Video Information
Views
874
Likes
2
Duration
26:51
Published
Feb 22, 2017
Related Trending Topics
LIVE TRENDSRelated trending topics. Click any trend to explore more videos.