Alan Turing: The Pioneer Who Launched Modern Computer Science 💻
Discover the life and groundbreaking contributions of Alan Turing, the mathematician and logician whose work laid the foundation for today's computers and artificial intelligence.

Unlock Mind
152 views • Dec 8, 2024
About this video
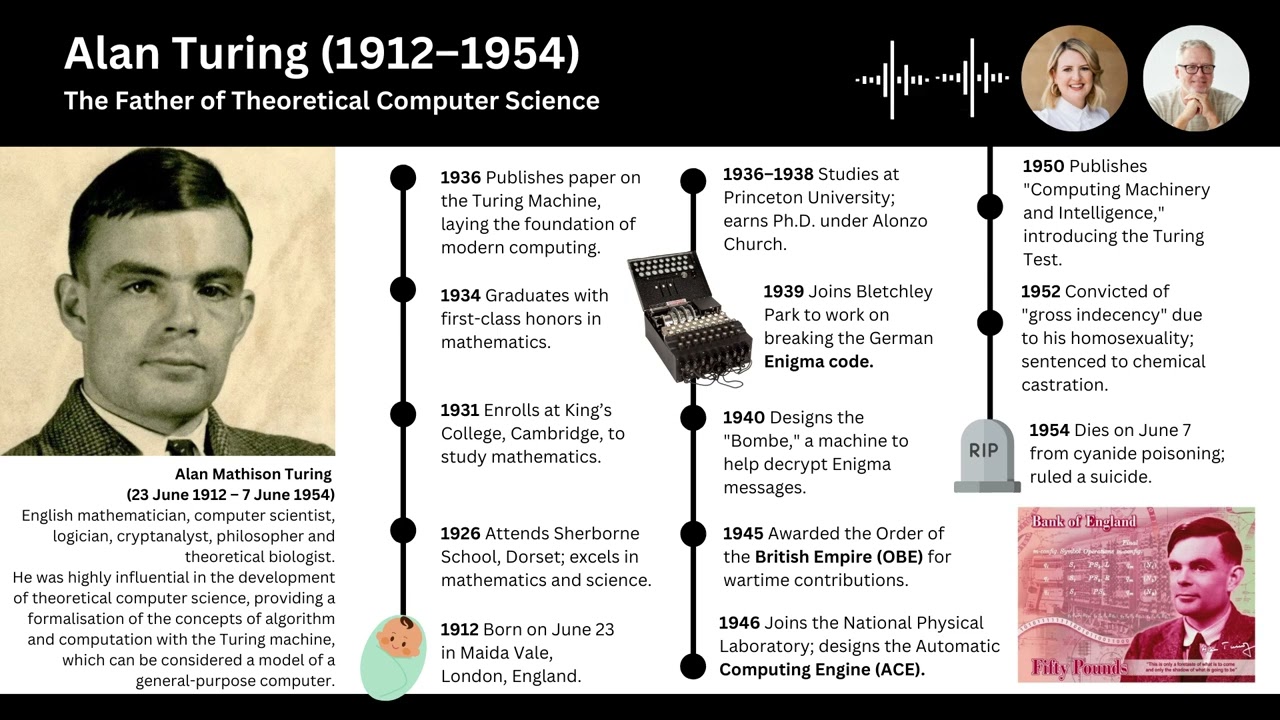
Alan Turing (1912–1954) was a British mathematician, logician, and computer scientist, widely regarded as the father of modern computer science and artificial intelligence. His groundbreaking work laid the foundation for many technologies we use today.
Key Contributions:
Turing Machine (1936):
Turing introduced the concept of the "Turing Machine," a theoretical device that could simulate any computational process. This idea formalized the concepts of algorithm and computation, forming the basis of computer science.
Codebreaking during WWII:
Turing worked at Bletchley Park, Britain's codebreaking center, where he played a crucial role in breaking the German Enigma cipher. His efforts significantly shortened the war and saved countless lives.
Turing Test (1950):
In his paper Computing Machinery and Intelligence, Turing proposed a test to determine if a machine could exhibit intelligent behavior indistinguishable from that of a human. This remains a central concept in AI research.
Early Computers:
Turing contributed to the development of some of the earliest computers, such as the Automatic Computing Engine (ACE), envisioning their potential to solve complex mathematical problems.
Legacy:
Despite his monumental contributions, Turing faced persecution due to his homosexuality, which was illegal in the UK at the time. He was convicted in 1952 and underwent chemical castration. Tragically, he died in 1954 under circumstances widely believed to be suicide.
In 2009, the UK government issued a formal apology for his treatment, and in 2013, Turing received a royal pardon. Today, his legacy is celebrated worldwide, with his name immortalized in awards, schools, and scientific institutions.
#biography #sciencepodcast #scientist #mathematician #computerscience #historyofscience
Key Contributions:
Turing Machine (1936):
Turing introduced the concept of the "Turing Machine," a theoretical device that could simulate any computational process. This idea formalized the concepts of algorithm and computation, forming the basis of computer science.
Codebreaking during WWII:
Turing worked at Bletchley Park, Britain's codebreaking center, where he played a crucial role in breaking the German Enigma cipher. His efforts significantly shortened the war and saved countless lives.
Turing Test (1950):
In his paper Computing Machinery and Intelligence, Turing proposed a test to determine if a machine could exhibit intelligent behavior indistinguishable from that of a human. This remains a central concept in AI research.
Early Computers:
Turing contributed to the development of some of the earliest computers, such as the Automatic Computing Engine (ACE), envisioning their potential to solve complex mathematical problems.
Legacy:
Despite his monumental contributions, Turing faced persecution due to his homosexuality, which was illegal in the UK at the time. He was convicted in 1952 and underwent chemical castration. Tragically, he died in 1954 under circumstances widely believed to be suicide.
In 2009, the UK government issued a formal apology for his treatment, and in 2013, Turing received a royal pardon. Today, his legacy is celebrated worldwide, with his name immortalized in awards, schools, and scientific institutions.
#biography #sciencepodcast #scientist #mathematician #computerscience #historyofscience
Video Information
Views
152
Likes
6
Duration
16:15
Published
Dec 8, 2024
Related Trending Topics
LIVE TRENDSRelated trending topics. Click any trend to explore more videos.